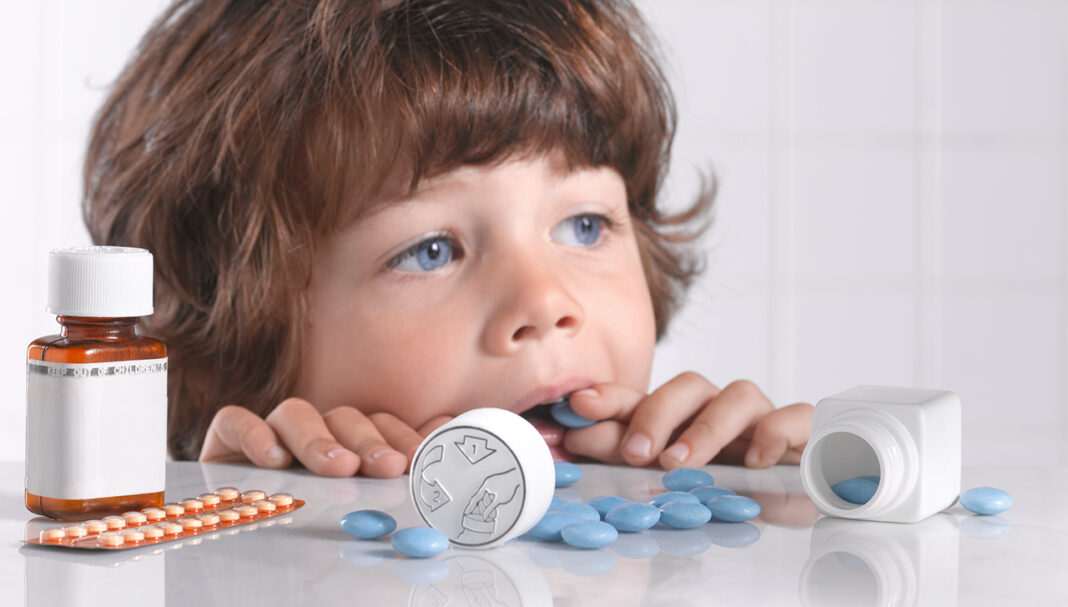
Case scenario

Joyce, 76, lives independently and takes seven regular medicines with various dosing frequencies. She struggles to manage her medicines, especially with frequent brand changes due to supply issues. To help herself remember, Joyce recently began placing her daily tablets in a dish on the kitchen bench. During a visit, her 6-year-old grandson mistook the tablets for lollies and was about to swallow them when he was stopped just in time. Joyce is shaken by the incident and distressed by what could have happened.
After reading this article, pharmacists should be able to:
Competency standards (2016) addressed: 1.1, 1.4, 1.5, 2.2, 3.1, 3.5 Accreditation number: CAP2508SYPSH Accreditation expiry: 31/07/2028 |
Already
THIS IS A CPD ARTICLE. YOU NEED TO BE A PSA MEMBER AND LOGGED IN TO READ MORE.



 Owner of Canberra's Capital Chemist Southlands Louise McLean MPS.[/caption]
Owner of Canberra's Capital Chemist Southlands Louise McLean MPS.[/caption]

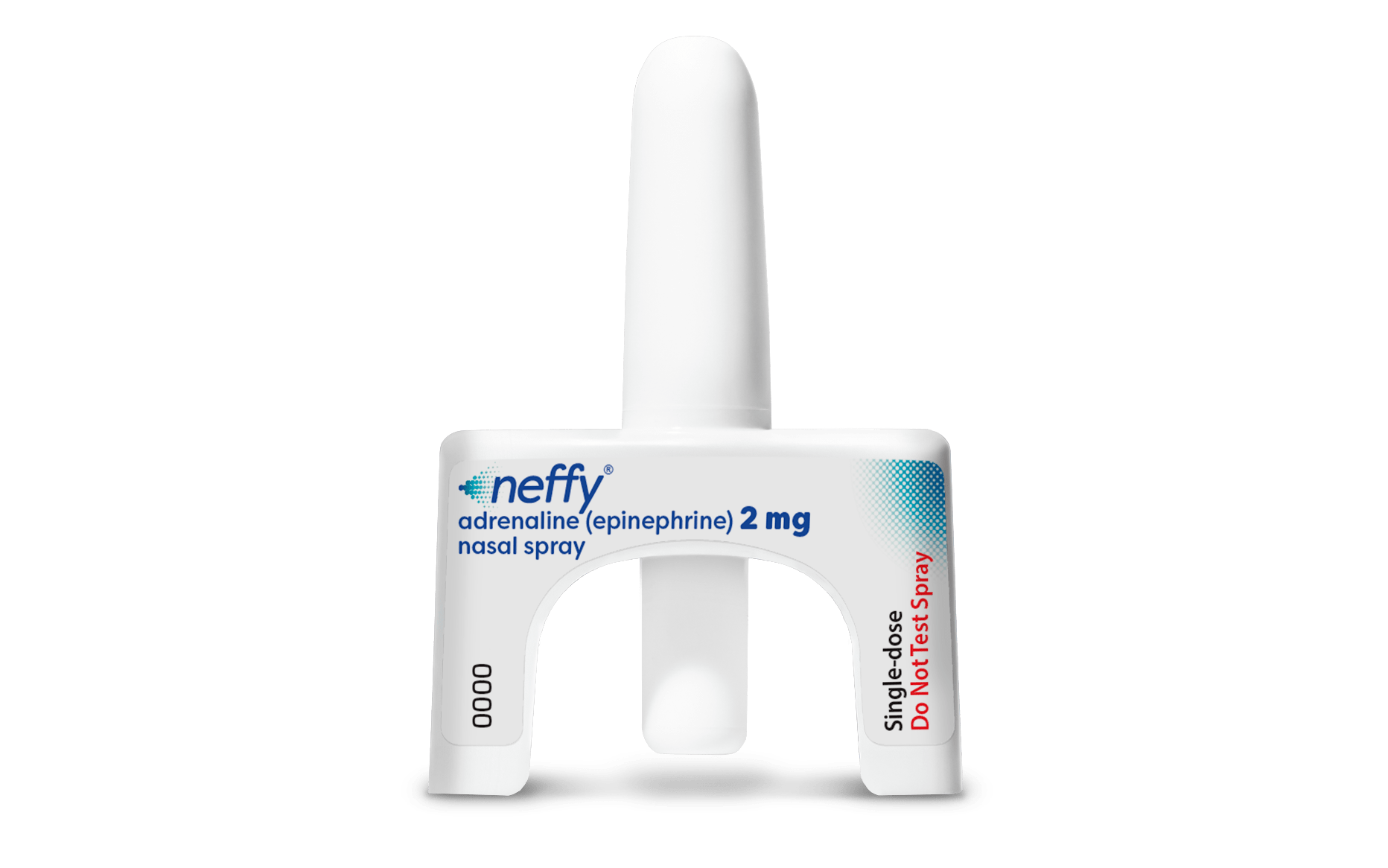 Supplied by CSL Seqirus[/caption]
Supplied by CSL Seqirus[/caption]

 Tahnee Simpson[/caption]
Tahnee Simpson[/caption]
 Nicolette Ellis MPS[/caption]
Nicolette Ellis MPS[/caption]