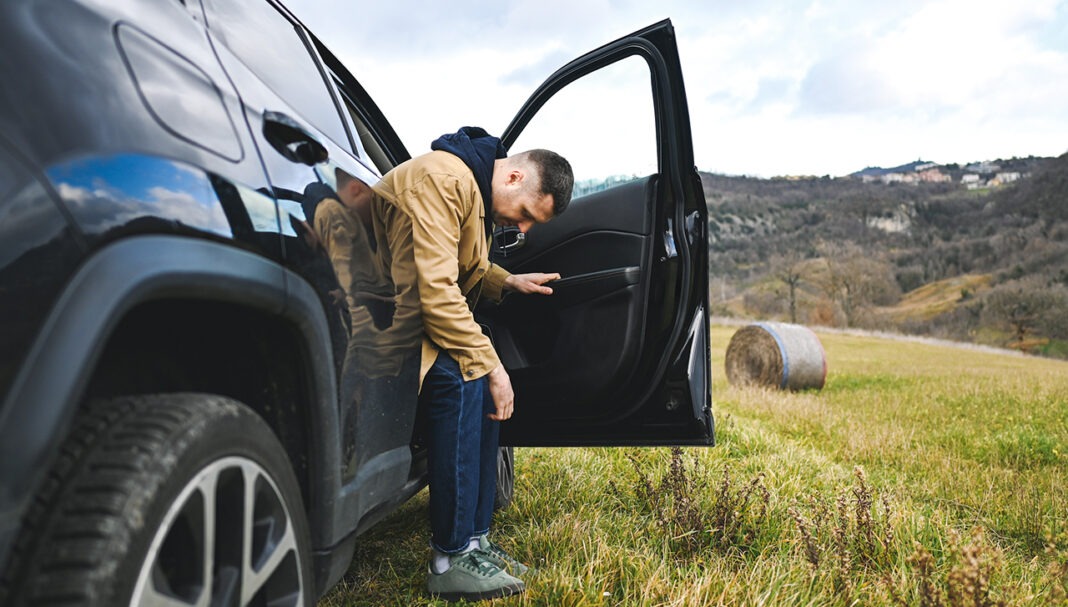
Case scenario
James, 28, comes to your pharmacy asking for advice on managing motion sickness ahead of a long car trip next weekend. He often feels nauseous and dizzy during longer journeys and wonders if there’s any medicine that can help.
Learning objectivesAfter reading this article, pharmacists should be able to:
Competencies addressed: 1.1, 1.4, 1.5, 2.2, 3.1, 3.5 Accreditation number: CAP2509SYPVS Accreditation expiry: 31/08/2028 |
Already read the CPD in the journal? Scroll to the bottom to SUBMIT ANSWERS.
Introduction
Motion sickness, also called travel sickness, is a common condition triggered by actual motion (e.g. travel by car, boat or plane) or perceived motion (e.g. through video games, movies or virtual reality).1 It typically presents with nausea and can be distressing and disruptive for those affected.
Pharmacists play a key role in the management of motion sickness by offering evidence-based advice, recommending appropriate non-pharmacological and pharmacological strategies, counselling patients on safe and effective use, and referring when necessary.
Epidemiology
Motion sickness can be experienced by nearly anyone with a functional vestibular system; however, individual susceptibility v
THIS IS A CPD ARTICLE. YOU NEED TO BE A PSA MEMBER AND LOGGED IN TO READ MORE.


 Ruth Nona[/caption]
Ruth Nona[/caption]
 Kate Gunthorpe MPS[/caption]
Kate Gunthorpe MPS[/caption]
 Madison Low[/caption]
Madison Low[/caption]


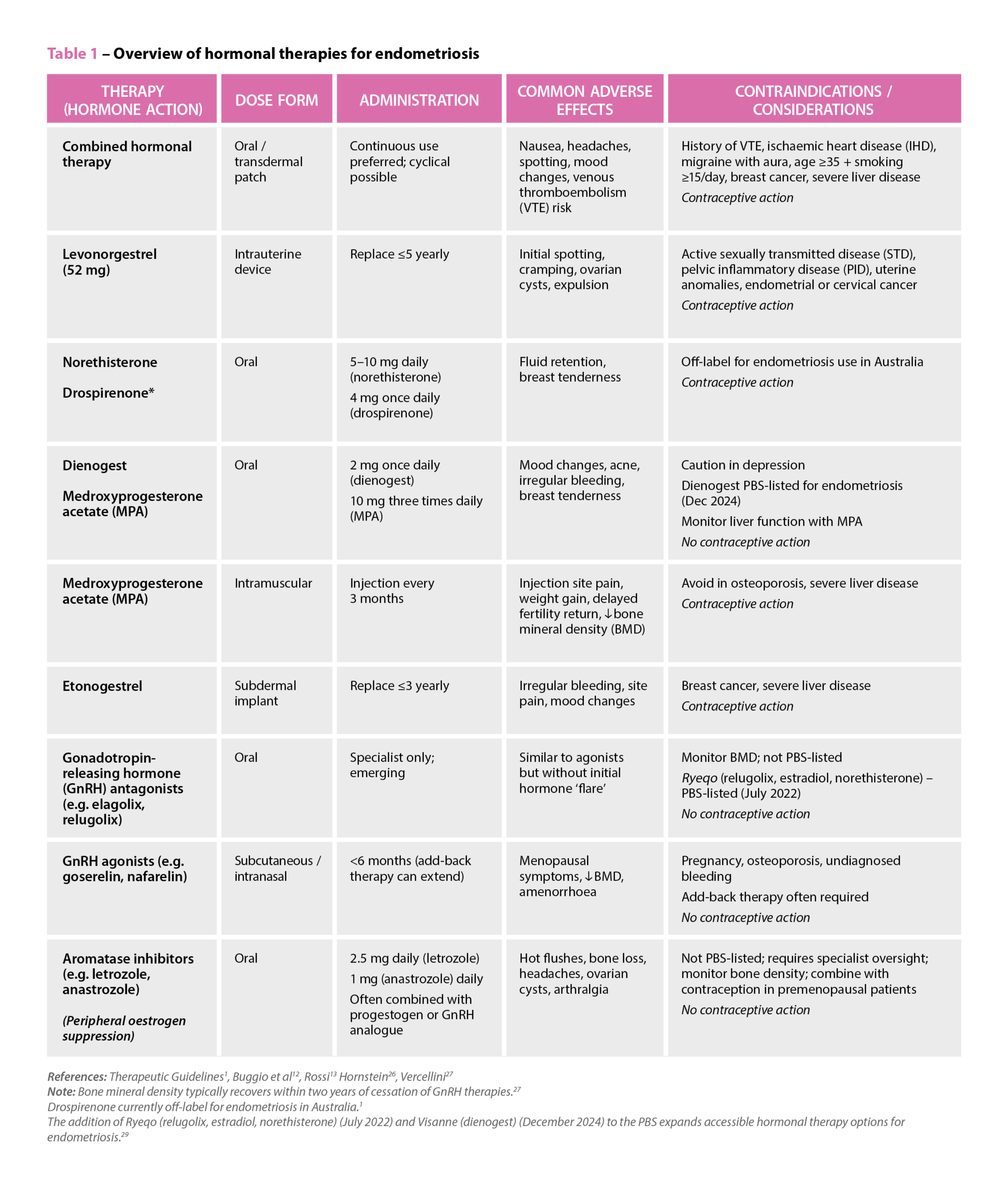 References: Therapeutic Guidelines
References: Therapeutic Guidelines