Case scenario
Luke is a 24-year-old male who visits your pharmacy with a repeat prescription for hydrocortisone and fludrocortisone tablets. He has been taking these medicines since being diagnosed with Addison’s disease during a recent hospital admission. Luke tells you that he is about to travel to Bali for a holiday and is worried about getting ‘Bali belly’, as he recently experienced food poisoning. On further discussion, you discover that Luke does not have a written sick-day plan and is unsure what ‘stress dosing’ means.
Learning objectivesAfter reading this article, pharmacists should be able to:
Competency (2016) standards addressed: 1.1, 1.4, 1.5, 2.2, 3.1, 3.5 Accreditation code: CAP2511CDMVN Accreditation expiry: 31/10/2028 |
Already read the CPD in the journal? Scroll to the bottom to SUBMIT ANSWERS.
Introduction
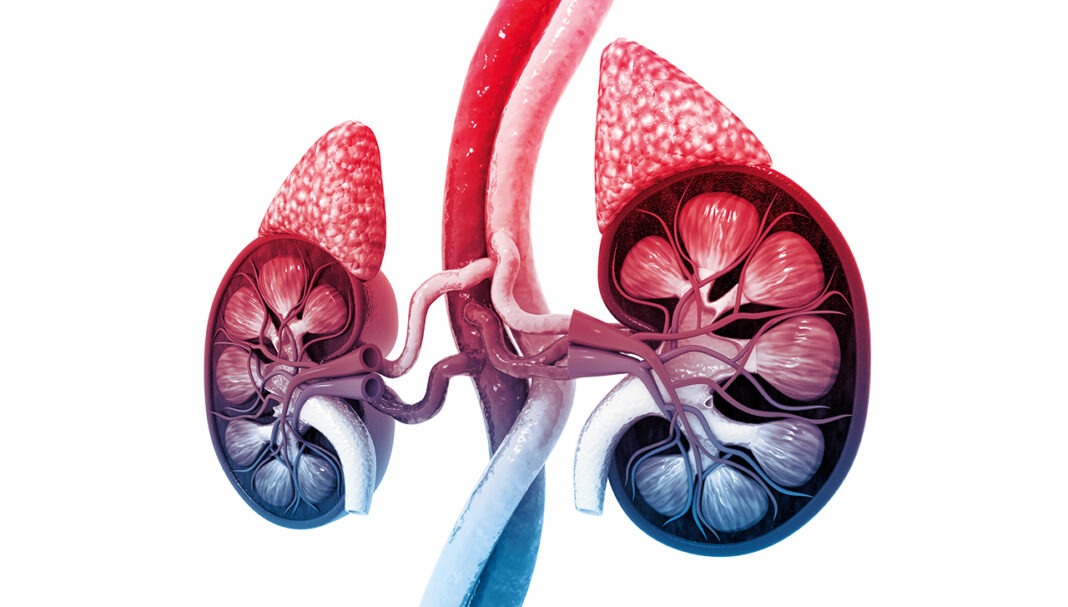
Adrenal insufficiency occurs when the adrenal glands don’t produce sufficient cortisol, a key hormone involved in metabolism and the body’s stress response. Depending on the underlying cause of adrenal insufficiency, other hormones such as aldosterone may also be affected.1 Patients with adrenal insufficiency typically require lifelong glucocorticoid replacement treatment, with dose adjustments required during periods o
THIS IS A CPD ARTICLE. YOU NEED TO BE A PSA MEMBER AND LOGGED IN TO READ MORE.



 Kelly Abbott MPS[/caption]
Kelly Abbott MPS[/caption]

 Owner of Canberra's Capital Chemist Southlands Louise McLean MPS.[/caption]
Owner of Canberra's Capital Chemist Southlands Louise McLean MPS.[/caption]