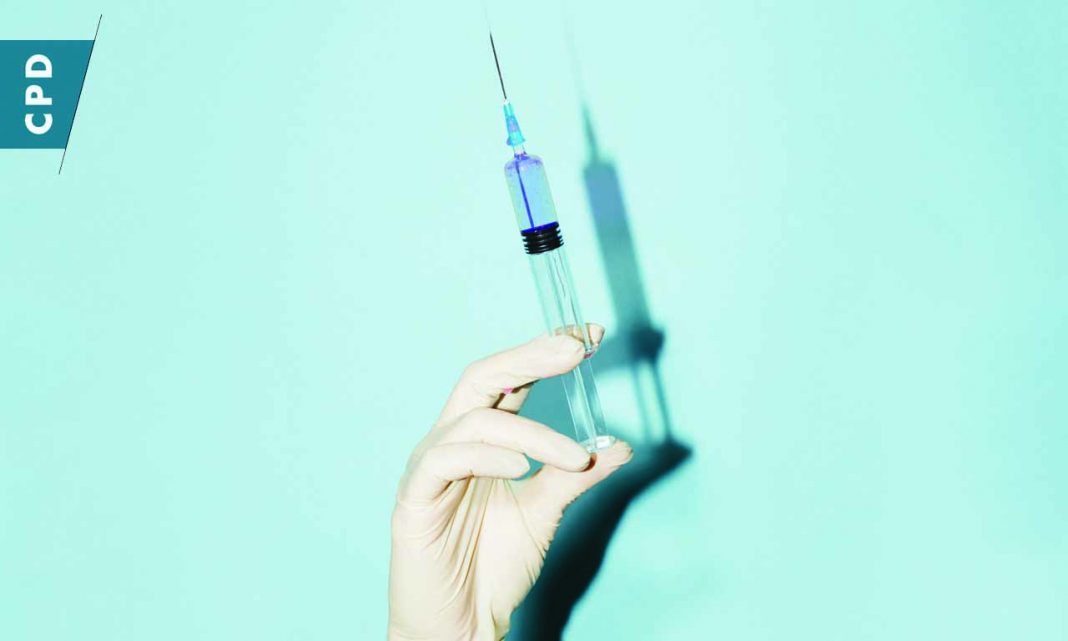
Meningococcal disease is an acute bacterial infection that can affect the brain and spinal cord (meningitis), or the blood (septicaemia); whilst some patients can have a combination of both.
| Learning objectives
After reading this article, pharmacists should be able to:
Competencies (2016) addressed: 3.1.1, 3.1.2, 3.2.2, 3.2.3, 3.2.5, 3.3.1, 3.5.1, 3.6.1, 3.6.2, 3.6.3. Competencies (2010) addressed: 4.2.1, 4.2.2, 4.3.3, 6.1.1, 6.2.1, 6.3.1, 6.3.3, 7.1.1, 7.1.2, 7.1.4, 7.2.2, 7.3.1. |
Case Scenario
Rafiq and his brother are planning a trip to Saudi Arabia to attend the annual Hajj. Rafiq has heard that serious outbreaks of meningitis have occurred in Saudi Arabia, and knows that meningococcal disease is infectious and serious. He would like to know whether his childhood vaccination against the disease would provide adequate cover during his trip.
Want to learn more? PSA members can access the full article and assessment questions here to earn up to 1.5 Group 2 CPD credits.
Not a PSA member? Find out why more than 18,000 pharmacists choose PSA to support, advance and create opportunities for the pharmacy career and the greater pharmacy profession. Click here to join today.


 John Jones MPS, pharmacist immuniser and owner of My Community Pharmacy Shortland in Newcastle, NSW[/caption]
John Jones MPS, pharmacist immuniser and owner of My Community Pharmacy Shortland in Newcastle, NSW[/caption]

 Debbie Rigby FPS explaining how to correctly use different inhaler devices[/caption]
Debbie Rigby FPS explaining how to correctly use different inhaler devices[/caption]



 Professor Sepehr Shakib[/caption]
Professor Sepehr Shakib[/caption]

 Lee McLennan MPS[/caption]
Lee McLennan MPS[/caption]
 Dr Natalie Soulsby FPS, Adv Prac Pharm[/caption]
Dr Natalie Soulsby FPS, Adv Prac Pharm[/caption]
 Joanne Gross MPS[/caption]
Joanne Gross MPS[/caption]