Case scenario
Josh, a 25-year-old student, presents to your pharmacy for his regular HIV PrEP repeat, and gives you a prescription for prochlorperazine 5 mg three times daily from a different prescriber. He asks to speak to you about ringing in his ears. He attended a music festival a few weeks ago but the ringing in his ears is more recent. You ask about any other symptoms, and he describes some vertigo and swollen lymph nodes. He had a painless ulcer in his mouth recently but thinks it has gone away. Josh takes no other medicines and has no allergies.
Learning objectivesAfter reading this article, pharmacists should be able to:
Competencies addressed: 1.1, 1.4, 1.5, 2.2, 3.1, 3.5 Accreditation number: CAP2509DMAD Accreditation expiry: 31/08/2028 |
Already read the CPD in the journal? Scroll to the bottom to SUBMIT ANSWERS.
Introduction
Syphilis is a preventable and curable sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacteria Treponema pallidum. Syphilis is often considered one of the more intriguing STIs due to its debated historical origins, varied clinical presentations across distinct stages, and its suspected diagnoses among writers and artists dating back to the 1500s.1
The organism is transmitted via close skin-to-skin contact. Although most cases are sexually acquired through unprotected oral, vaginal or anal sex, the infection can also be vertically transmitted, resulting in congenital syphilis where T
THIS IS A CPD ARTICLE. YOU NEED TO BE A PSA MEMBER AND LOGGED IN TO READ MORE.


 Ruth Nona[/caption]
Ruth Nona[/caption]
 Kate Gunthorpe MPS[/caption]
Kate Gunthorpe MPS[/caption]
 Madison Low[/caption]
Madison Low[/caption]


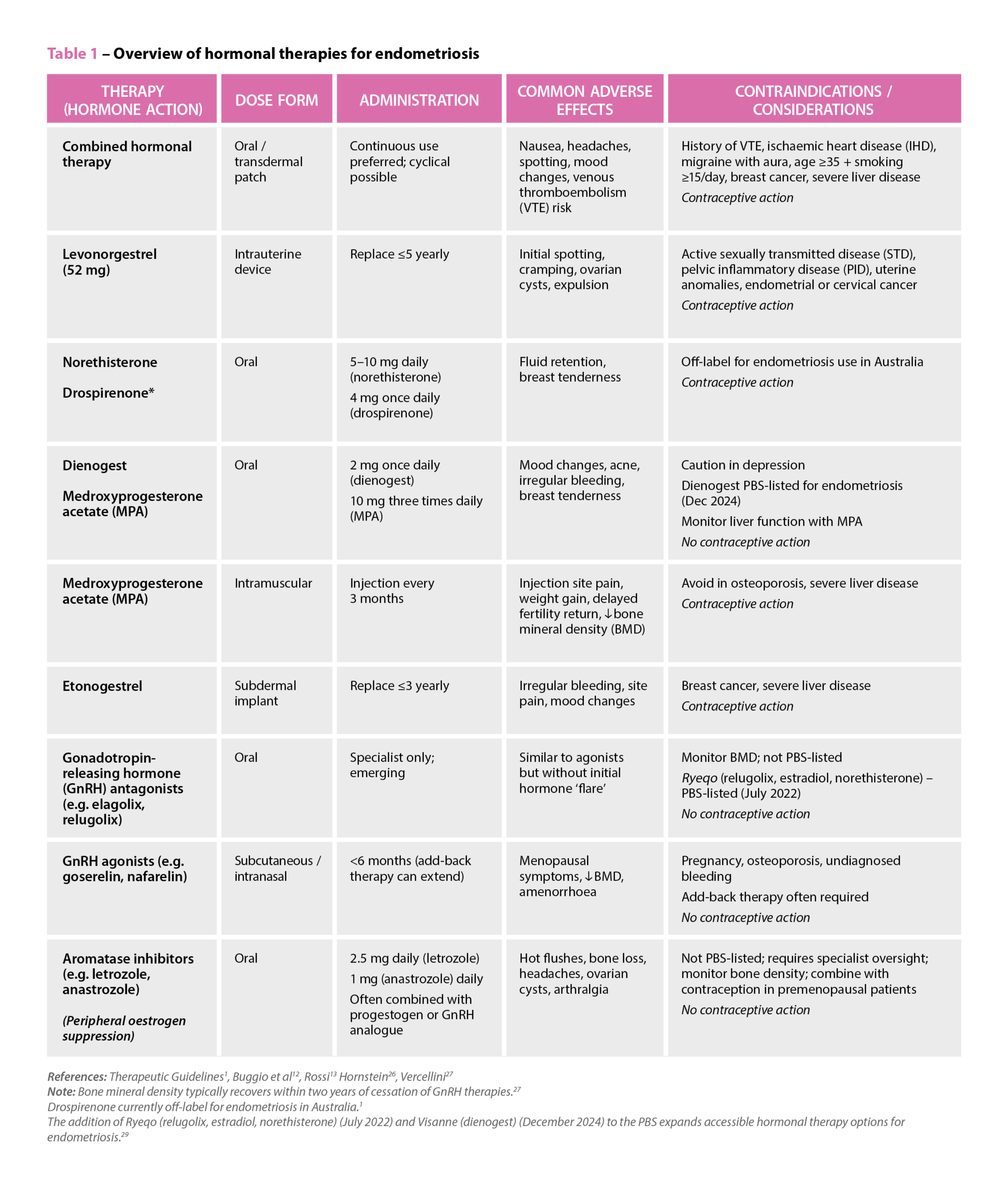 References: Therapeutic Guidelines
References: Therapeutic Guidelines