References
- UpToDate. The common cold in adults: Treatment and prevention. 2024. At: www.uptodate.com/contents/the-common-cold-in-adults-treatment-and-prevention?search=the%20common%20cold%20in%20adults&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1
- Pasioti M, Maggina P, Megremis S, et al. The common cold: potential for future prevention or cure. Current allergy and asthma reports 2014;14:413.
- Allan GM, Arroll B. Prevention and treatment of the common cold: making sense of the evidence. Cmaj 2014;186(3):190–9.
- Jackson Allen P, Simenson S. Management of common cold symptoms with over-the-counter medications: clearing the confusion. Postgrad Med 2013;125(1):73–81.
- Nault D, Machingo TA, Shipper AG, et al. Zinc for prevention and treatment of the common cold. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2024;5(5):Cd014914.
- Mayo Clinic. Zinc. 2024. At: www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements-zinc/art-20366112


 Ruth Nona[/caption]
Ruth Nona[/caption]
 Kate Gunthorpe MPS[/caption]
Kate Gunthorpe MPS[/caption]
 Madison Low[/caption]
Madison Low[/caption]


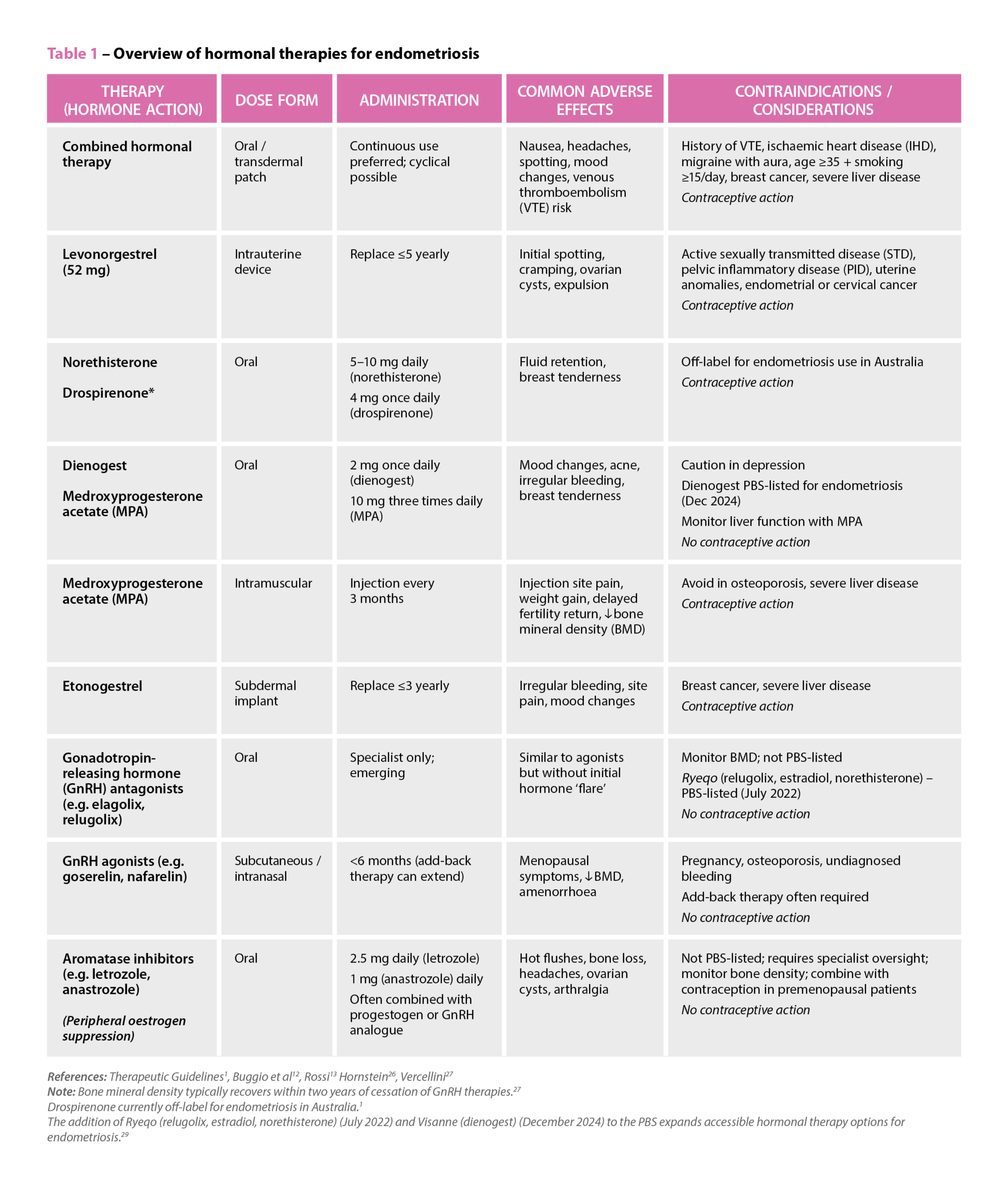 References: Therapeutic Guidelines
References: Therapeutic Guidelines