td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31238
[post_author] => 6804
[post_date] => 2026-01-28 14:00:38
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-28 03:00:38
[post_content] => Australia's Minister for Health has announced a National Medicines Record. What is it, and what will it achieve?
Medicine safety has long depended on pharmacists making critical decisions with incomplete information. As prescribing becomes increasingly fragmented across face-to-face care, telehealth and digital platforms, those gaps are widening – with serious consequences for patients.
Reforms announced by Minister for Health and Ageing Mark Butler this morning aim to address this issue, eventually leading to a National Medicines Record.
The announcement follows advocacy by Alison Collins after the death of her daughter Erin, who died in 2024 after being prescribed medicines through multiple digital health platforms without a complete view of her medical history.
Erin’s story
Erin was 24 years old and had been taking multiple medicines for her mental health. She had been hospitalised multiple times for problems stemming from medicine misuse and was placed on daily staged supply pickup of her medicines.
The hospital care teams were so concerned they placed multiple warning messages in her My Health Record. However, these warnings were not accessed by telehealth services or local pharmacies prior to her fatal overdose.
Erin’s case highlighted systemic vulnerabilities that pharmacists have warned about for years, particularly as digital prescribing expands faster than the safeguards designed to support safe, coordinated care.
The first step
Initially, the reforms would require all medicines information from online prescribers to be uploaded to My Health Record For pharmacists, this will make a fuller picture of all the medicines a patient has been prescribed more visible. This is critical given the increasing number of prescribers an individual may have with the rise of telehealth and condition-specific providers.
Under the proposed changes, medicines prescribed and dispensed through online platforms – including the clinical context for prescribing – would be made available through My Health Record. This is intended to help reduce the risk of medicine errors, adverse drug reactions and inappropriate use by ensuring healthcare professionals have access to more complete and timely information.
The path to a National Medicines Record
The reforms also commit the Government to designing and developing a National Medicines Record using existing digital health infrastructure, including electronic prescribing, the Active Script List and My Health Record.
While details are still emerging, the proposal has the potential to address a core challenge for pharmacists: how to identify and resolve medicines-related risks without a reliable, up-to-date picture of a patient’s full medicines history.
Welcoming the announcement, PSA National President Professor Mark Naunton MPS noted it aligns with the profession's long standing advocacy.
'Pharmacists have consistently sought better-connected digital health systems to improve patient safety with medicines. It’s something PSA has been advocating for over many years, including through our flagship medicine safety report series,” Prof. Naunton said.
'Access to a more complete and reliable medicines record has the potential to significantly improve patient safety and strengthen clinical decision-making.'
'The announcement is fully aligned with PSA’s ongoing advocacy to improve medicines safety systems and ensure pharmacists are supported as medicines experts across all settings of care,' he continued.
'PSA will engage in the consultation for these proposals and continue to work with the Government to support system improvements that make medicine use in Australia safer.'
A consultation period is now underway to guide the inclusion of medicines information from all online prescribers by default, with the first phase expected to be completed by December 2026. The Government has also flagged ongoing enhancements to the 1800MEDICARE app to support medicines management.
[post_title] => What a National Medicines Record might mean for patient safety and pharmacy practice
[post_excerpt] => Australia's Minister for Health has announced a National Medicines Record. What is it, and what will it achieve?
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => towards-a-national-medicines-record
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-30 16:02:41
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-30 05:02:41
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31238
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => What a National Medicines Record might mean for patient safety and pharmacy practice
[title] => What a National Medicines Record might mean for patient safety and pharmacy practice
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/towards-a-national-medicines-record/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31240
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31221
[post_author] => 3410
[post_date] => 2026-01-27 10:42:14
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-26 23:42:14
[post_content] => Community pharmacist Deborah Williams reflects on 7 years working at the Chemist Warehouse Australian Open pop-up pharmacy, sharing what makes event-based practice unique, the presentations she sees most often, and why adaptability is essential outside the traditional pharmacy setting.
How is running a pop-up pharmacy at the Australian Open different from your day-to-day practice?
The pop-up pharmacy at the Australian Open (AO) differs from practising in a community pharmacy such as Eltham, primarily because of the tools and therapeutic options available.
At the AO, we don’t have access to Schedule 4 medicines, and there are even additional restrictions imposed on over-the-counter medicines by the tournament. Certain Pharmacist Only products we would routinely recommend in a community setting aren’t permitted, particularly medicines that may cause drowsiness or could be perceived as performance-enhancing. This significantly changes how symptom management is approached.
The patient demographic is also very different. We see a large number of international visitors and cruise passengers who may only be in Australia briefly and often present with immediate, short-term needs – for example, sleep disruption, pain, minor illness, dehydration or general discomfort after long travel. There are frequent situations where a medicine that would be clinically appropriate in a normal pharmacy setting simply isn’t an option at the AO, so you have to think laterally and focus on non-sedating, non-restricted alternatives and practical advice. The pop-up pharmacy also operates with a deliberately limited range selection, so you rely far more on clinical judgement, counselling and problem-solving than product depth.
Despite these constraints, the service has been extremely well received. In earlier years, many people were genuinely surprised that a pharmacy service was available at all, and the level of appreciation was very high. Over time, as the service has become established, patrons have come to actively expect that level of healthcare support onsite – which speaks to how valuable it has proven to be.
Ultimately, while the setting is very different, the core role remains the same: providing accessible, safe short-term healthcare support. At the AO, that simply requires a more adaptive and creative approach within tighter boundaries.
Why did you first put your hand up for this roster 7 years ago?
Largely because tennis is a big part of our family life. My two daughters are avid tennis players, and I’ve spent a lot of time travelling with them to tournaments – both around Australia and internationally. So the opportunity to be involved in the AO and to experience tennis from a different perspective was very appealing.
At the time, the chance to be part of a pop-up pharmacy within a major sporting event felt unique. Working in an environment where the energy is high and where people are genuinely excited to be there was a strong motivator. It also offered the opportunity to step outside the traditional four walls of community pharmacy and apply my skills in a different, fast-paced setting.
[caption id="attachment_31227" align="aligncenter" width="600"]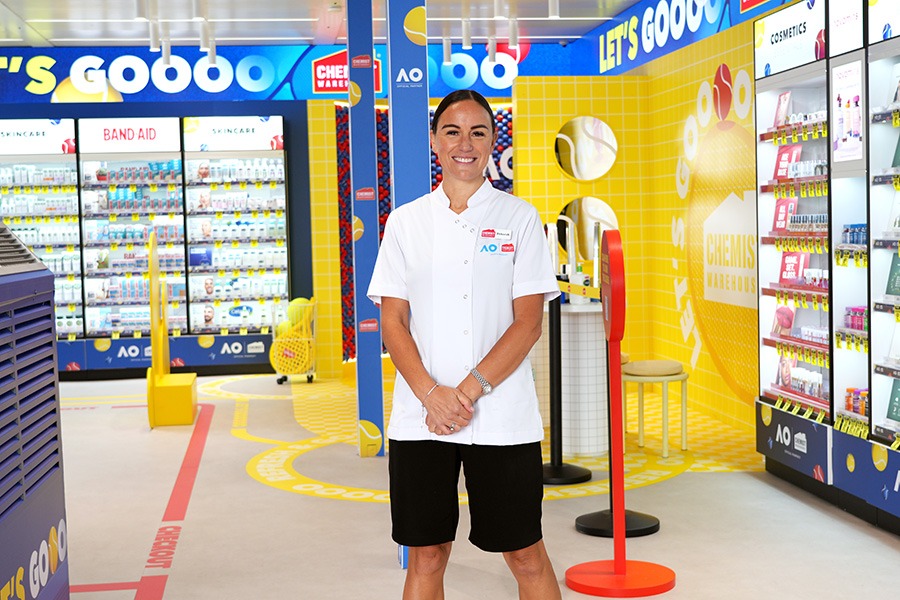 Deborah Williams at the Chemist Warehouse Australian Open pop-up pharmacy[/caption]
I’ve previously worked as a pharmacist at other large-scale events, including the Grand Prix and the Colour Run, and I’ve always enjoyed that style of practice. You see different patient groups and presentations, and there’s a strong focus on immediate, practical healthcare support. Combining that type of work with a sport that’s already such a big part of my life made the AO an easy decision.
Deborah Williams at the Chemist Warehouse Australian Open pop-up pharmacy[/caption]
I’ve previously worked as a pharmacist at other large-scale events, including the Grand Prix and the Colour Run, and I’ve always enjoyed that style of practice. You see different patient groups and presentations, and there’s a strong focus on immediate, practical healthcare support. Combining that type of work with a sport that’s already such a big part of my life made the AO an easy decision.
What are the most common presentations you deal with?
They vary from year to year, often reflecting broader environmental and public health factors.
In early years, respiratory presentations were prominent, with high demand for salbutamol due to smoke exposure following severe bushfires. During the COVID-19 pandemic, testing-related requests and symptomatic presentations dominated, with many people seeking advice for fever, cough, fatigue and isolation management. Across all years, heat-related conditions are consistently common. We see significant sunburn, dehydration, headaches and heat exhaustion – with many patrons initially attributing symptoms solely to sun exposure. Being able to distinguish between sunburn, heat exhaustion and early heat stroke is a critical part of the role.
Other frequent presentations include viral infections, gastrointestinal upset, reflux and heartburn related to food and alcohol consumption – as well as general pain and discomfort from long days on site.
Overall, the role involves managing acute, short-term presentations in a high-heat, high-activity environment, where timely assessment, clear advice and appropriate escalation are essential.
What has been your best experience working at the AO?
The cumulative nature of the role over many years. Being invited back repeatedly reflects the value of having pharmacists in a high-profile, high-pressure environment.
But one particularly rewarding aspect has been the behind-the-scenes clinical role. While players rarely attend the pharmacy, their support staff and assistants frequently seek advice on their behalf. That often involves real-time discussions, sometimes over the phone, where clinical judgement, clarity and discretion are critical. The trust placed in pharmacists in those moments is significant.
Knowing that the advice provided may contribute, even in a small way, to a player’s comfort, recovery or ability to perform is professionally satisfying. It reinforces the role of pharmacists as accessible healthcare professionals who can deliver practical, timely support in environments where precision matters.
What are the most popular products with tennis fans?
Those that address the practical realities of spending long hours outdoors and walking significant distances, often in warm conditions.
Blister management products are consistently in high demand, particularly protective dressings and treatments for foot friction. Sun exposure also drives strong demand for post-sunburn and skin-soothing treatments, as well as products to manage heat-related discomfort.
Gastrointestinal support is another common category, with antacid and reflux treatments frequently requested, often related to food choices, heat and prolonged time on site.
Hydration support products are also very popular, particularly oral rehydration formulations for patrons experiencing fatigue, headaches or dehydration. Simple analgesics for pain and headache management are frequently requested as well.
‘Knowing that the advice provided may contribute, even in a small way, to a player’s comfort, recovery or ability to perform is professionally satisfying.'
deborah williams
And convenient nutritional snacks, particularly protein bars, are consistently popular, reflecting the need for quick, portable options that support energy levels throughout the day. Personal care essentials such as deodorant are also commonly requested, given the length and physical nature of the event.
Who is your favourite tennis player?
For many years my favourite player was Rafael Nadal. Beyond his extraordinary achievements on court, what stood out most was his character. He has a genuine never-say-die attitude, combined with humility and respect for everyone around him. Behind the scenes he was approachable, carried his own bags, acknowledged volunteers and staff, and treated people with quiet respect – which left a lasting impression.
More recently, I’ve really enjoyed watching Alex de Minaur. His speed, work rate and relentless court coverage are exceptional – and he brings an intensity and competitiveness that’s exciting to watch. He represents a very grounded, hardworking style of tennis that resonates strongly with Australian fans.
Do you have any tips for pharmacists working at the AO this summer?
Embrace the environment and enjoy the opportunity to practise pharmacy in a different setting. The atmosphere is energetic and positive, and people genuinely want your advice, making the role both enjoyable and rewarding.
From a professional perspective, be prepared to think beyond products. With a diverse, transient population, many interactions involve problem-solving rather than dispensing. That may mean offering practical health advice, directing people to appropriate medical services, or helping them navigate local healthcare options.
It’s also important to remember that you are representing both your profession and the event itself, so clear communication, professionalism and sound judgement matter. Finally, take the time to experience the event. Use breaks to watch some tennis or explore the precinct. Being part of the Australian Open is a unique opportunity, and enjoying the atmosphere helps you bring energy and perspective back into your role.
[post_title] => Pharmacy on centre court
[post_excerpt] => Limited medicines options and time-critical presentations push pharmacists at the Australian Open to practise at the top of their skills.
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => pharmacy-on-centre-court
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-27 15:01:46
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-27 04:01:46
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31221
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => Pharmacy on centre court
[title] => Pharmacy on centre court
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/pharmacy-on-centre-court/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31226
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31216
[post_author] => 9164
[post_date] => 2026-01-27 09:50:51
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-26 22:50:51
[post_content] => The PSA congratulates Emeritus Professor Colin Burton Chapman and Dipak Sanghvi of Victoria on being appointed a Member of the Order of Australia (AM) as part of the 2026 Australia Day Honours.
Emeritus Prof Colin Chapman has been recognised with the AM for significant service to pharmacy and pharmaceutical science research, education and practice.
Mr Sanghvi was recognised with the AM for significant service to community health through governance and board roles.
The PSA also extended its congratulations to Rhys Hollington London, Bruce Vincent Townsend, and Maurice Alan Renshaw on being awarded the Medal of the Order of Australia (OAM).
Mr Hollington London has been recognised with the OAM for service to the community of Wynyard, Tasmania.
Mr Townsend was recognised with the OAM for service to the community of Raymond Terrace, NSW.
Mr Renshaw, also from NSW, was recognised with the OAM for service to the pharmaceutical industry.
The PSA National President Professor Mark Naunton MPS acknowledged the high honour of this recognition and thanked the recipients for their previous and ongoing contributions to the pharmacy profession.
‘It is evident that pharmacists play a vital role in their communities and the healthcare system. To have multiple pharmacists recognised on the prestigious Australia Day Honours List is a phenomenal outcome,’ Prof Naunton said.
‘On behalf of PSA and the pharmacy profession, I would like to extend my congratulations to Emeritus Prof Chapman, Mr Sanghvi, Mr Hollington London, Mr Vincent and Mr Renshaw on their well-deserved recognition.’
[post_title] => National recognition for pharmacists on Australia Day
[post_excerpt] => The PSA congratulates the pharmacists who were recognised as part on this year's Australia Day Honours List.
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => national-recognition-for-pharmacists-on-australia-day
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-27 15:02:15
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-27 04:02:15
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31216
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => National recognition for pharmacists on Australia Day
[title] => National recognition for pharmacists on Australia Day
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/national-recognition-for-pharmacists-on-australia-day/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31220
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31206
[post_author] => 3410
[post_date] => 2026-01-21 10:52:56
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-20 23:52:56
[post_content] => Holiday crowds bring unique clinical challenges, testing pharmacists’ problem-solving skills from sun exposure injuries to urgent medicine gaps.
In many metropolitan areas, January is a lull period for pharmacists – as city dwellers head out of town to beat the heat and reset for the year ahead. But not so in many regional beachside areas, with pharmacies experiencing a steady uptick in visiting clientele, as Rebecca Davies, who works as a community pharmacist in Cotton Tree on Queensland's Sunshine Coast, would attest.
‘Where I'm working at the moment is right on the beach, so it's literally busy all the time,’ said Ms Davies, who was formerly based in Mona Vale on Sydney’s Northern Beaches. ‘I wouldn't say there's ever a quiet time, as in the winter, we still get people coming up from the southern states for holidays.’
With a caravan park stationed down the road, nearby units that are typically rented out during peak holiday periods and warm weather year-round, it’s a matter of balancing the holiday trade that’s passing through with regular customers.
A clinical mix by the sea
Alongside routine dispensing and chronic disease management for locals, managing beach-related enquiries and conditions is a part of everyday practice.
Over-the-counter demand increases during holiday periods, with visitors seeking sunscreens, beach equipment and first-aid items, with many presentations requiring pharmacist oversight.
[caption id="attachment_31212" align="aligncenter" width="441"]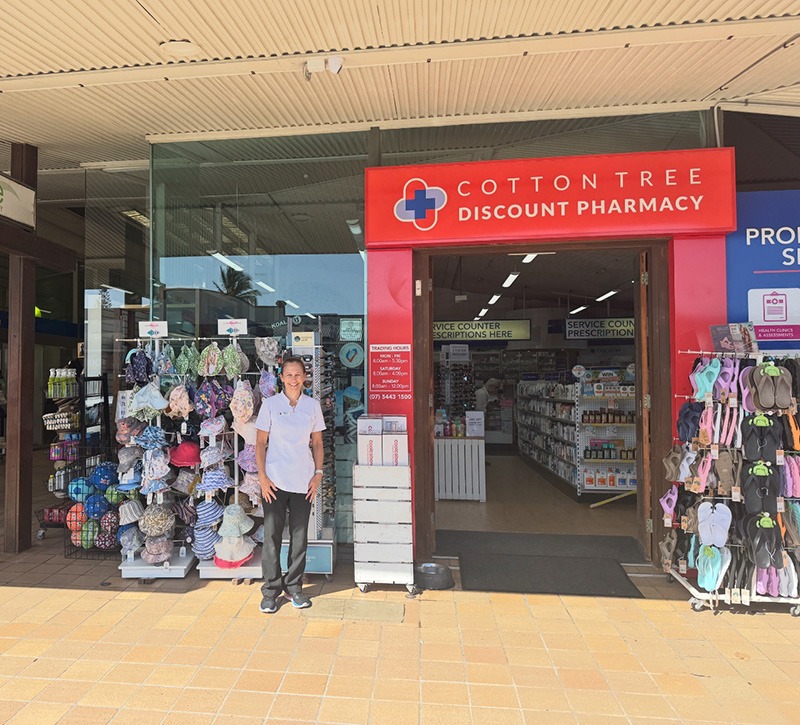 Rebecca Davies[/caption]
‘You get people that aren’t used to the sun that come in with sunburn,’ Ms Davies said.
Children feature prominently, particularly those visiting from interstate or overseas – presenting with significant sunburn, dehydration or injuries sustained during outdoor play.
‘The kids that come from places that aren’t used to the beaches come in with the sunburn,’ she said. ‘Then there are the holiday kids [who’ve fallen off] bikes or skateboards.’
In one recent case, a teenage girl presented with extensive sunburn that had initially been treated in the pharmacy. Several days later, she returned with worsening symptoms.
‘She came back about 5 days later and it looked like she’d picked up a bacterial infection from broken skin.’
At that point, Ms Davies referred the patient to a doctor, recognising that pharmacy management was no longer sufficient. ‘It had just gone too far for anything that we could do for her.’
Marine-related skin reactions are another frequent presentation, particularly sea lice, which can ‘get caught in between the swimmers and their skin’.
Management usually involves antihistamines, topical corticosteroids and practical advice to reduce symptoms.
‘You tell them to keep the area cool,’ Ms Davies said. ‘Anything that makes them hotter will make it worse.’
In most cases, these conditions can be managed entirely in-store, allowing patients to avoid medical appointments during short stays.
‘But there's a lot of regular customers and we still have all the Webster-paks among other things to manage,’ she said.
Rebecca Davies[/caption]
‘You get people that aren’t used to the sun that come in with sunburn,’ Ms Davies said.
Children feature prominently, particularly those visiting from interstate or overseas – presenting with significant sunburn, dehydration or injuries sustained during outdoor play.
‘The kids that come from places that aren’t used to the beaches come in with the sunburn,’ she said. ‘Then there are the holiday kids [who’ve fallen off] bikes or skateboards.’
In one recent case, a teenage girl presented with extensive sunburn that had initially been treated in the pharmacy. Several days later, she returned with worsening symptoms.
‘She came back about 5 days later and it looked like she’d picked up a bacterial infection from broken skin.’
At that point, Ms Davies referred the patient to a doctor, recognising that pharmacy management was no longer sufficient. ‘It had just gone too far for anything that we could do for her.’
Marine-related skin reactions are another frequent presentation, particularly sea lice, which can ‘get caught in between the swimmers and their skin’.
Management usually involves antihistamines, topical corticosteroids and practical advice to reduce symptoms.
‘You tell them to keep the area cool,’ Ms Davies said. ‘Anything that makes them hotter will make it worse.’
In most cases, these conditions can be managed entirely in-store, allowing patients to avoid medical appointments during short stays.
‘But there's a lot of regular customers and we still have all the Webster-paks among other things to manage,’ she said.
Managing forgotten medicines
Beyond acute injuries and skin conditions, medicine continuity for holidaymakers is one of the most complex challenges Ms Davies faces.
Tourists frequently arrive without sufficient medicine supply, having forgotten it at home or miscalculating how long they would be away.
‘it’s quite satisfying to help someone who is on their holidays by keeping it running smoothly and taking the stress out of it.'
rebecca davies
‘If the customer has a regular pharmacy at home, we can contact that pharmacy,’ she said. ‘They can fax scripts and post the originals.’
Electronic prescriptions have made this process significantly easier.
‘With eScripts, it’s really easy to sign them up to the Active Script List and have access to all their eScripts online,’ Ms Davies said.
However, not all situations are quickly resolved.
‘I had one customer the other day who’d left her medicine at home and didn’t have a script,’ she said.
The medicine was venlafaxine, which should not be stopped abruptly.
In this particular situation, the best course of action was for the patient to arrange an urgent medical consultation with their regular GP, or via an online telehealth provider if necessary.
‘I encourage people to stay with their regular doctor. But there are times when those services are very useful.’
Managing medicines for visiting patients often requires Ms Davies to look beyond her own dispensary.
‘If we don’t have the medication and it’s for someone passing through, ordering it in isn’t always a possibility, because the person might move on before it comes in,’ she said.
‘So we’ll ring the other pharmacies around to see if they’ve got it and direct the patient there. It’s just about trying to source the medication for the patient before they move on.’
Expanded scope makes a difference on holiday
Expanded scope of practice services have proven particularly valuable in a tourist-heavy setting, especially pharmacist-led treatment for uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs).
‘Patients with symptoms of a UTI who have come here for the weekend can come into the pharmacy quite distressed,’ Ms Davies said. ‘The symptoms of the infection really disrupt how they get through the day and they’re not familiar with the area or the doctors.’
Being able to assess and treat eligible patients in the pharmacy can significantly reduce discomfort and disruption.
‘It definitely puts them at ease when we go through that, that list of when we can and can't supply,’ Ms Davies said. ‘We can say, “Yes, we can help you”.’
For visitors, the impact is immediate.
‘They’re not wasting 24 to 48 hours trying to figure out where to go,’ she said. ‘It makes a big difference to their holiday.’
According to Ms Davies, community awareness of pharmacist UTI services has increased, with many patients now presenting specifically requesting assessment rather than symptom-only treatments.
‘More people come in already knowing that the service exists rather than asking for Ural,’ she said.
Staffing for constant demand
Maintaining service quality during sustained busy periods requires careful staff management.
‘Sometimes the owner puts more staff on over the holiday period. Because obviously there’s going to be an influx of tourists, there’s a couple of extra staff we can call on,’ Ms Davies said.
‘The business also supports private clinics, so we have access to extra staff we can call on during the day if things start to back up.’
The pharmacy relies on a mix of permanent staff, casual pharmacists, students and graduates to manage peaks. Having experienced casual staff who can be called in at short notice is particularly valuable.
‘We’re lucky to have someone we can call on who used to be a permanent employee and now works casually,’ she said.
Despite the intensity, Ms Davies finds the work highly rewarding.
‘It definitely tests your knowledge on how to navigate certain situations,’ she said. ‘And it’s quite satisfying to help someone who is on their holidays by keeping it running smoothly and taking the stress out of it.’
For pharmacists considering a move to a coastal area, Rebecca sees beachside practice as challenging but professionally enriching.
‘It offers lots of different scenarios for helping patients compared to your regular customer coming in with the same things from month to month,’ she said. ‘And there’s lots of opportunities for problem-solving.’
Help patients avoid serious sunburn by completing the AP CPD: Sun safety, don’t feel the burn.
Image licensed under Creative Commons.
[post_title] => Practising pharmacy where others vacation
[post_excerpt] => Holiday crowds bring unique clinical challenges for beachside pharmacy practice, from sun exposure injuries to urgent medicine gaps.
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => practising-pharmacy-where-others-vacation
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-21 15:53:15
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-21 04:53:15
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31206
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => Practising pharmacy where others vacation
[title] => Practising pharmacy where others vacation
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/practising-pharmacy-where-others-vacation/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31209
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31190
[post_author] => 3410
[post_date] => 2026-01-19 11:11:00
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-19 00:11:00
[post_content] => A recent systematic review published in the BMJ has reignited debate about what happens when patients stop taking glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) and related GLP-1–based incretin therapies.
The analysis found that weight often returns quickly once treatment is discontinued – in some cases faster than with other weight-loss interventions.
And it’s not just weight that rebounds. Cardiometabolic risk markers, including blood pressure, blood glucose and blood lipids, were also found to revert towards pre-treatment levels.
As prescribing of these medicines continues to rise, the findings raise a broader question: should patients be starting these medicines in the first place?
AP spoke with experts to unpack the evidence.
Weight regain predictable, but not the real problem
Professor Clare Collins, Professor of Nutrition and Dietetics at the University of Newcastle, said the pattern of rapid weight regain following cessation was entirely unsurprising.
‘This is exactly what you would expect,’ she said.
[caption id="attachment_31196" align="aligncenter" width="400"]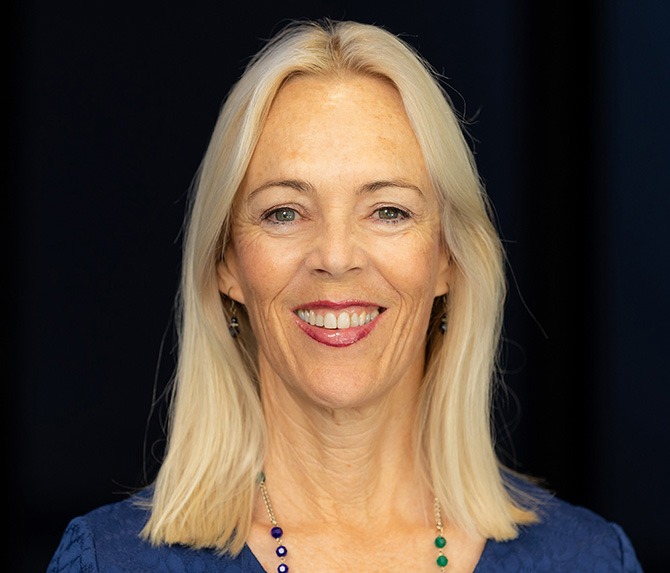 Professor Clare Collins[/caption]
For Prof Collins, the findings reinforce a core principle of chronic disease management: when an effective treatment is withdrawn, the condition it was controlling usually returns.
‘If someone stops taking antihypertensives, what happens? Their blood pressure goes back up,’ she said.
Professor Clare Collins[/caption]
For Prof Collins, the findings reinforce a core principle of chronic disease management: when an effective treatment is withdrawn, the condition it was controlling usually returns.
‘If someone stops taking antihypertensives, what happens? Their blood pressure goes back up,’ she said.
‘While predictable, the deterioration back to baseline is why we need to be thinking much more carefully about what is needed for long-term maintenance.'
Prof clare collins
While weight regain attracts headlines, Prof Collins said the more clinically concerning signal is the deterioration in metabolic markers once treatment ceases.
‘While predictable, the deterioration back to baseline is why we need to be thinking much more carefully about what is needed for long-term maintenance.’
Not a sign of treatment failure
Associate Professor Trevor Steward, Director of the Melbourne School of Psychological Sciences’ Brain and Mental Health Hub, agrees that the rebound effect reflects how GLP-1 RA medicines work, rather than a failure of the drugs or patient behaviour.
Instead of creating permanent physiological change, GLP-1 RAs amplify hormonal signals that already exist in the body – particularly those involved in appetite regulation, digestion and satiety. The benefits seen during treatment depend on sustained exposure to these hormones.
[caption id="attachment_31197" align="aligncenter" width="400"]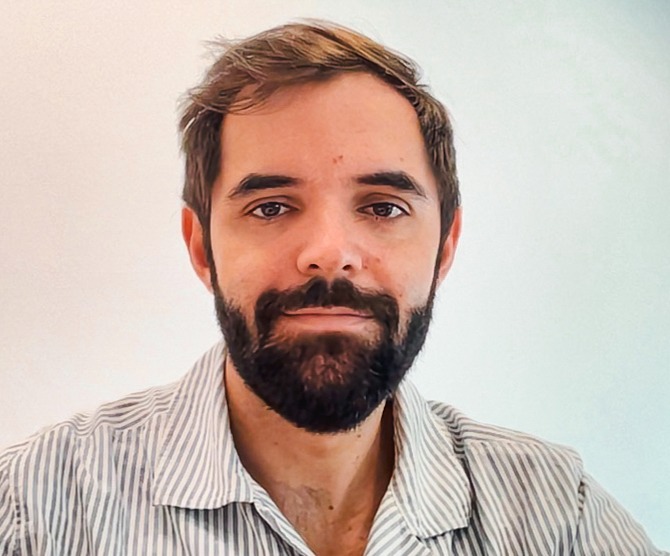 Associate Professor Trevor Steward[/caption]
‘That's why we see this rapid rebound effect of people experiencing weight gain when they stop using them, because there’s no longer increased circulating levels of hormones impacting their different body systems,’ A/Prof Steward said.
However, the mechanisms behind the accelerated regain are not yet fully understood.
‘Some indications are that while these newer medications help people lose weight faster, they may cause a stronger slingshot effect,’ he said.
Prof Collins points to emerging evidence suggesting incretin therapies cross the blood–brain barrier, influencing reward pathways linked to appetite and environmental cues to eat.
‘For example, if you go to the supermarket for a loaf of bread and come back with donuts too – that’s what’s referred to as “food noise”,’ she said. ‘Some people say this [noise] really goes down when using these therapies.’
When treatment is withdrawn, the surrounding food environment can quickly reassert itself. This is where tapering, behavioural support and nutrition strategies become critical.
‘It may be that people are more receptive to maintenance support programs as they’re tapering or finding out what their maintenance medication dose is,’ she said. ‘If they’re aware of that point, they’ll recognise when the food noise starts again.’
Associate Professor Trevor Steward[/caption]
‘That's why we see this rapid rebound effect of people experiencing weight gain when they stop using them, because there’s no longer increased circulating levels of hormones impacting their different body systems,’ A/Prof Steward said.
However, the mechanisms behind the accelerated regain are not yet fully understood.
‘Some indications are that while these newer medications help people lose weight faster, they may cause a stronger slingshot effect,’ he said.
Prof Collins points to emerging evidence suggesting incretin therapies cross the blood–brain barrier, influencing reward pathways linked to appetite and environmental cues to eat.
‘For example, if you go to the supermarket for a loaf of bread and come back with donuts too – that’s what’s referred to as “food noise”,’ she said. ‘Some people say this [noise] really goes down when using these therapies.’
When treatment is withdrawn, the surrounding food environment can quickly reassert itself. This is where tapering, behavioural support and nutrition strategies become critical.
‘It may be that people are more receptive to maintenance support programs as they’re tapering or finding out what their maintenance medication dose is,’ she said. ‘If they’re aware of that point, they’ll recognise when the food noise starts again.’
Nutrition: the missing variable
Prof Collins recently led a systematic review which highlighted that changes in dietary intake and nutrition remain largely invisible in incretin trials.
‘Of all the phase three trials, only two actually measured and reported what people ate,’ she said.
Most trials provided standardised advice but did not collect data on dietary intake, leaving clinicians to infer how appetite suppression, nausea and early satiety shaped eating patterns over time.
‘They mostly worked with people to identify dietary changes that would remove about 2,000 kilojoules a day – enough to trigger weight loss,’ she said.
But reduced intake doesn’t automatically equate to improved diet quality or nutrient adequacy, with micronutrient deficiencies and loss of lean mass emerging if nutrition isn’t actively monitored.
With frequent patient contact, Prof Collins believes pharmacists are uniquely placed to identify emerging problems, intervene early and support appropriate referral to dietitians for medical nutrition therapy.
‘[And] if pharmacy staff are trained, they can say, “Hang on a minute, you need to talk to the pharmacist”.’
The University of Newcastle also has a suite of resources pharmacists could direct patients to, including a healthy eating quiz and obesity management podcast, available here.
When visible deterioration or rapid weight loss appears, referral becomes essential. ‘Once you think, “this person is fading before our eyes”, that’s when you alert the GP and refer to a dietitian,’ Prof Collins said.
Supporting persistence with therapy also plays a role in outcomes.
‘The main benefit isn’t weight – it’s metabolic health,’ she said. ‘Helping people manage [adverse] effects supports continuation.’
As weight loss occurs, pharmacists should also be alert to the need to review other medicines.
‘If someone is dropping weight rapidly, blood sugars and blood pressure can fall,’ she said. ‘There are also rare but potentially severe complications – pancreatitis, gallstones, bowel obstruction and non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy,’ she said. ‘Staying well hydrated is critical – urine should look straw-coloured.’
Playing the long game
A/Prof Steward said there’s now sufficient evidence to normalise weight regain after cessation. And given the established risks associated with long-term obesity, he suggests continued therapy may represent a lower-risk option for some patients.
‘As we know, having a very high BMI for a long period of time confers its own levels of risks in terms of cardiovascular disease and other issues,’ he said. ‘So [many clinicians] think it's worth staying on these [medicines] long term as opposed to the potential risk of weight [regain].’
For people with repeated cycles of weight loss and regain, A/Prof Steward said GLP-1 RAs are increasingly being understood as potentially lifelong treatments – similar to medicines used for other chronic conditions.
‘Clinicians want clearer evidence around tapering and maintenance – and right now, they’re operating in the dark.'
A/prof trevor steward
‘I recently had a conversation with someone who has lost over 50 kilograms three times in her life,’ he said. ‘After a sustained period of lifestyle change, the weight still comes back. She would rather stay on these medicines for life than put her body through that cycle again.’
As use expands, A/Prof Steward emphasised the importance of clarifying intent and expectations before treatment begins.
‘It's really important to have that conversation with a pharmacist or GP about whether they want to make that commitment to potentially taking these long term,’ he said.
This also creates space to explore motivations for initiating therapy.
‘A lot of people are taking these medications for non-health related reasons, e.g. if they have a wedding coming up,’ A/Prof Steward said.
‘So it's really worth emphasising that these medications are serious drugs that impact the entire body, and it's not something that should be frivolously taken for the purpose of losing a few kg in a month – only to just have them come back.’
While Prof Collins doesn’t think the BMJ findings should deter prescribing, she said cost must be contextualised early – particularly as maintenance strategies continue to evolve. This may include lower costs associated with food and other medicines.
‘If you're improving your weight-related health, how much would medical visits have cost if your health hadn’t improved?’ she said. ‘These medications are a long-term cost, like a car or a mobile phone. We also don't yet know whether, for some people, they may be able to have periods where they don't take it and then reinitiate at lower doses again.’
With potential PBS listings and new formulations on the horizon, A/Prof Steward said clinical messaging will need to evolve alongside the evidence.
‘Over half a million Australians are now taking these medicines,’ he said. ‘Clinicians want clearer evidence around tapering and maintenance – and right now, they’re operating in the dark.’
For more information, read the AP CPD article Weight loss management.
[post_title] => Are GLP-1 RAs becoming lifelong medicines?
[post_excerpt] => A recent systematic review has reignited debate about what happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 RAs and related incretin therapies.
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => are-glp-1-ras-becoming-lifelong-medicines
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-19 15:35:39
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-19 04:35:39
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31190
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => Are GLP-1 RAs becoming lifelong medicines?
[title] => Are GLP-1 RAs becoming lifelong medicines?
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/are-glp-1-ras-becoming-lifelong-medicines/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31192
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31238
[post_author] => 6804
[post_date] => 2026-01-28 14:00:38
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-28 03:00:38
[post_content] => Australia's Minister for Health has announced a National Medicines Record. What is it, and what will it achieve?
Medicine safety has long depended on pharmacists making critical decisions with incomplete information. As prescribing becomes increasingly fragmented across face-to-face care, telehealth and digital platforms, those gaps are widening – with serious consequences for patients.
Reforms announced by Minister for Health and Ageing Mark Butler this morning aim to address this issue, eventually leading to a National Medicines Record.
The announcement follows advocacy by Alison Collins after the death of her daughter Erin, who died in 2024 after being prescribed medicines through multiple digital health platforms without a complete view of her medical history.
Erin’s story
Erin was 24 years old and had been taking multiple medicines for her mental health. She had been hospitalised multiple times for problems stemming from medicine misuse and was placed on daily staged supply pickup of her medicines.
The hospital care teams were so concerned they placed multiple warning messages in her My Health Record. However, these warnings were not accessed by telehealth services or local pharmacies prior to her fatal overdose.
Erin’s case highlighted systemic vulnerabilities that pharmacists have warned about for years, particularly as digital prescribing expands faster than the safeguards designed to support safe, coordinated care.
The first step
Initially, the reforms would require all medicines information from online prescribers to be uploaded to My Health Record For pharmacists, this will make a fuller picture of all the medicines a patient has been prescribed more visible. This is critical given the increasing number of prescribers an individual may have with the rise of telehealth and condition-specific providers.
Under the proposed changes, medicines prescribed and dispensed through online platforms – including the clinical context for prescribing – would be made available through My Health Record. This is intended to help reduce the risk of medicine errors, adverse drug reactions and inappropriate use by ensuring healthcare professionals have access to more complete and timely information.
The path to a National Medicines Record
The reforms also commit the Government to designing and developing a National Medicines Record using existing digital health infrastructure, including electronic prescribing, the Active Script List and My Health Record.
While details are still emerging, the proposal has the potential to address a core challenge for pharmacists: how to identify and resolve medicines-related risks without a reliable, up-to-date picture of a patient’s full medicines history.
Welcoming the announcement, PSA National President Professor Mark Naunton MPS noted it aligns with the profession's long standing advocacy.
'Pharmacists have consistently sought better-connected digital health systems to improve patient safety with medicines. It’s something PSA has been advocating for over many years, including through our flagship medicine safety report series,” Prof. Naunton said.
'Access to a more complete and reliable medicines record has the potential to significantly improve patient safety and strengthen clinical decision-making.'
'The announcement is fully aligned with PSA’s ongoing advocacy to improve medicines safety systems and ensure pharmacists are supported as medicines experts across all settings of care,' he continued.
'PSA will engage in the consultation for these proposals and continue to work with the Government to support system improvements that make medicine use in Australia safer.'
A consultation period is now underway to guide the inclusion of medicines information from all online prescribers by default, with the first phase expected to be completed by December 2026. The Government has also flagged ongoing enhancements to the 1800MEDICARE app to support medicines management.
[post_title] => What a National Medicines Record might mean for patient safety and pharmacy practice
[post_excerpt] => Australia's Minister for Health has announced a National Medicines Record. What is it, and what will it achieve?
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => towards-a-national-medicines-record
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-30 16:02:41
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-30 05:02:41
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31238
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => What a National Medicines Record might mean for patient safety and pharmacy practice
[title] => What a National Medicines Record might mean for patient safety and pharmacy practice
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/towards-a-national-medicines-record/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31240
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31221
[post_author] => 3410
[post_date] => 2026-01-27 10:42:14
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-26 23:42:14
[post_content] => Community pharmacist Deborah Williams reflects on 7 years working at the Chemist Warehouse Australian Open pop-up pharmacy, sharing what makes event-based practice unique, the presentations she sees most often, and why adaptability is essential outside the traditional pharmacy setting.
How is running a pop-up pharmacy at the Australian Open different from your day-to-day practice?
The pop-up pharmacy at the Australian Open (AO) differs from practising in a community pharmacy such as Eltham, primarily because of the tools and therapeutic options available.
At the AO, we don’t have access to Schedule 4 medicines, and there are even additional restrictions imposed on over-the-counter medicines by the tournament. Certain Pharmacist Only products we would routinely recommend in a community setting aren’t permitted, particularly medicines that may cause drowsiness or could be perceived as performance-enhancing. This significantly changes how symptom management is approached.
The patient demographic is also very different. We see a large number of international visitors and cruise passengers who may only be in Australia briefly and often present with immediate, short-term needs – for example, sleep disruption, pain, minor illness, dehydration or general discomfort after long travel. There are frequent situations where a medicine that would be clinically appropriate in a normal pharmacy setting simply isn’t an option at the AO, so you have to think laterally and focus on non-sedating, non-restricted alternatives and practical advice. The pop-up pharmacy also operates with a deliberately limited range selection, so you rely far more on clinical judgement, counselling and problem-solving than product depth.
Despite these constraints, the service has been extremely well received. In earlier years, many people were genuinely surprised that a pharmacy service was available at all, and the level of appreciation was very high. Over time, as the service has become established, patrons have come to actively expect that level of healthcare support onsite – which speaks to how valuable it has proven to be.
Ultimately, while the setting is very different, the core role remains the same: providing accessible, safe short-term healthcare support. At the AO, that simply requires a more adaptive and creative approach within tighter boundaries.
Why did you first put your hand up for this roster 7 years ago?
Largely because tennis is a big part of our family life. My two daughters are avid tennis players, and I’ve spent a lot of time travelling with them to tournaments – both around Australia and internationally. So the opportunity to be involved in the AO and to experience tennis from a different perspective was very appealing.
At the time, the chance to be part of a pop-up pharmacy within a major sporting event felt unique. Working in an environment where the energy is high and where people are genuinely excited to be there was a strong motivator. It also offered the opportunity to step outside the traditional four walls of community pharmacy and apply my skills in a different, fast-paced setting.
[caption id="attachment_31227" align="aligncenter" width="600"] Deborah Williams at the Chemist Warehouse Australian Open pop-up pharmacy[/caption]
I’ve previously worked as a pharmacist at other large-scale events, including the Grand Prix and the Colour Run, and I’ve always enjoyed that style of practice. You see different patient groups and presentations, and there’s a strong focus on immediate, practical healthcare support. Combining that type of work with a sport that’s already such a big part of my life made the AO an easy decision.
Deborah Williams at the Chemist Warehouse Australian Open pop-up pharmacy[/caption]
I’ve previously worked as a pharmacist at other large-scale events, including the Grand Prix and the Colour Run, and I’ve always enjoyed that style of practice. You see different patient groups and presentations, and there’s a strong focus on immediate, practical healthcare support. Combining that type of work with a sport that’s already such a big part of my life made the AO an easy decision.
What are the most common presentations you deal with?
They vary from year to year, often reflecting broader environmental and public health factors.
In early years, respiratory presentations were prominent, with high demand for salbutamol due to smoke exposure following severe bushfires. During the COVID-19 pandemic, testing-related requests and symptomatic presentations dominated, with many people seeking advice for fever, cough, fatigue and isolation management. Across all years, heat-related conditions are consistently common. We see significant sunburn, dehydration, headaches and heat exhaustion – with many patrons initially attributing symptoms solely to sun exposure. Being able to distinguish between sunburn, heat exhaustion and early heat stroke is a critical part of the role.
Other frequent presentations include viral infections, gastrointestinal upset, reflux and heartburn related to food and alcohol consumption – as well as general pain and discomfort from long days on site.
Overall, the role involves managing acute, short-term presentations in a high-heat, high-activity environment, where timely assessment, clear advice and appropriate escalation are essential.
What has been your best experience working at the AO?
The cumulative nature of the role over many years. Being invited back repeatedly reflects the value of having pharmacists in a high-profile, high-pressure environment.
But one particularly rewarding aspect has been the behind-the-scenes clinical role. While players rarely attend the pharmacy, their support staff and assistants frequently seek advice on their behalf. That often involves real-time discussions, sometimes over the phone, where clinical judgement, clarity and discretion are critical. The trust placed in pharmacists in those moments is significant.
Knowing that the advice provided may contribute, even in a small way, to a player’s comfort, recovery or ability to perform is professionally satisfying. It reinforces the role of pharmacists as accessible healthcare professionals who can deliver practical, timely support in environments where precision matters.
What are the most popular products with tennis fans?
Those that address the practical realities of spending long hours outdoors and walking significant distances, often in warm conditions.
Blister management products are consistently in high demand, particularly protective dressings and treatments for foot friction. Sun exposure also drives strong demand for post-sunburn and skin-soothing treatments, as well as products to manage heat-related discomfort.
Gastrointestinal support is another common category, with antacid and reflux treatments frequently requested, often related to food choices, heat and prolonged time on site.
Hydration support products are also very popular, particularly oral rehydration formulations for patrons experiencing fatigue, headaches or dehydration. Simple analgesics for pain and headache management are frequently requested as well.
‘Knowing that the advice provided may contribute, even in a small way, to a player’s comfort, recovery or ability to perform is professionally satisfying.'
deborah williams
And convenient nutritional snacks, particularly protein bars, are consistently popular, reflecting the need for quick, portable options that support energy levels throughout the day. Personal care essentials such as deodorant are also commonly requested, given the length and physical nature of the event.
Who is your favourite tennis player?
For many years my favourite player was Rafael Nadal. Beyond his extraordinary achievements on court, what stood out most was his character. He has a genuine never-say-die attitude, combined with humility and respect for everyone around him. Behind the scenes he was approachable, carried his own bags, acknowledged volunteers and staff, and treated people with quiet respect – which left a lasting impression.
More recently, I’ve really enjoyed watching Alex de Minaur. His speed, work rate and relentless court coverage are exceptional – and he brings an intensity and competitiveness that’s exciting to watch. He represents a very grounded, hardworking style of tennis that resonates strongly with Australian fans.
Do you have any tips for pharmacists working at the AO this summer?
Embrace the environment and enjoy the opportunity to practise pharmacy in a different setting. The atmosphere is energetic and positive, and people genuinely want your advice, making the role both enjoyable and rewarding.
From a professional perspective, be prepared to think beyond products. With a diverse, transient population, many interactions involve problem-solving rather than dispensing. That may mean offering practical health advice, directing people to appropriate medical services, or helping them navigate local healthcare options.
It’s also important to remember that you are representing both your profession and the event itself, so clear communication, professionalism and sound judgement matter. Finally, take the time to experience the event. Use breaks to watch some tennis or explore the precinct. Being part of the Australian Open is a unique opportunity, and enjoying the atmosphere helps you bring energy and perspective back into your role.
[post_title] => Pharmacy on centre court
[post_excerpt] => Limited medicines options and time-critical presentations push pharmacists at the Australian Open to practise at the top of their skills.
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => pharmacy-on-centre-court
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-27 15:01:46
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-27 04:01:46
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31221
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => Pharmacy on centre court
[title] => Pharmacy on centre court
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/pharmacy-on-centre-court/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31226
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31216
[post_author] => 9164
[post_date] => 2026-01-27 09:50:51
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-26 22:50:51
[post_content] => The PSA congratulates Emeritus Professor Colin Burton Chapman and Dipak Sanghvi of Victoria on being appointed a Member of the Order of Australia (AM) as part of the 2026 Australia Day Honours.
Emeritus Prof Colin Chapman has been recognised with the AM for significant service to pharmacy and pharmaceutical science research, education and practice.
Mr Sanghvi was recognised with the AM for significant service to community health through governance and board roles.
The PSA also extended its congratulations to Rhys Hollington London, Bruce Vincent Townsend, and Maurice Alan Renshaw on being awarded the Medal of the Order of Australia (OAM).
Mr Hollington London has been recognised with the OAM for service to the community of Wynyard, Tasmania.
Mr Townsend was recognised with the OAM for service to the community of Raymond Terrace, NSW.
Mr Renshaw, also from NSW, was recognised with the OAM for service to the pharmaceutical industry.
The PSA National President Professor Mark Naunton MPS acknowledged the high honour of this recognition and thanked the recipients for their previous and ongoing contributions to the pharmacy profession.
‘It is evident that pharmacists play a vital role in their communities and the healthcare system. To have multiple pharmacists recognised on the prestigious Australia Day Honours List is a phenomenal outcome,’ Prof Naunton said.
‘On behalf of PSA and the pharmacy profession, I would like to extend my congratulations to Emeritus Prof Chapman, Mr Sanghvi, Mr Hollington London, Mr Vincent and Mr Renshaw on their well-deserved recognition.’
[post_title] => National recognition for pharmacists on Australia Day
[post_excerpt] => The PSA congratulates the pharmacists who were recognised as part on this year's Australia Day Honours List.
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => national-recognition-for-pharmacists-on-australia-day
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-27 15:02:15
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-27 04:02:15
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31216
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => National recognition for pharmacists on Australia Day
[title] => National recognition for pharmacists on Australia Day
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/national-recognition-for-pharmacists-on-australia-day/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31220
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31206
[post_author] => 3410
[post_date] => 2026-01-21 10:52:56
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-20 23:52:56
[post_content] => Holiday crowds bring unique clinical challenges, testing pharmacists’ problem-solving skills from sun exposure injuries to urgent medicine gaps.
In many metropolitan areas, January is a lull period for pharmacists – as city dwellers head out of town to beat the heat and reset for the year ahead. But not so in many regional beachside areas, with pharmacies experiencing a steady uptick in visiting clientele, as Rebecca Davies, who works as a community pharmacist in Cotton Tree on Queensland's Sunshine Coast, would attest.
‘Where I'm working at the moment is right on the beach, so it's literally busy all the time,’ said Ms Davies, who was formerly based in Mona Vale on Sydney’s Northern Beaches. ‘I wouldn't say there's ever a quiet time, as in the winter, we still get people coming up from the southern states for holidays.’
With a caravan park stationed down the road, nearby units that are typically rented out during peak holiday periods and warm weather year-round, it’s a matter of balancing the holiday trade that’s passing through with regular customers.
A clinical mix by the sea
Alongside routine dispensing and chronic disease management for locals, managing beach-related enquiries and conditions is a part of everyday practice.
Over-the-counter demand increases during holiday periods, with visitors seeking sunscreens, beach equipment and first-aid items, with many presentations requiring pharmacist oversight.
[caption id="attachment_31212" align="aligncenter" width="441"] Rebecca Davies[/caption]
‘You get people that aren’t used to the sun that come in with sunburn,’ Ms Davies said.
Children feature prominently, particularly those visiting from interstate or overseas – presenting with significant sunburn, dehydration or injuries sustained during outdoor play.
‘The kids that come from places that aren’t used to the beaches come in with the sunburn,’ she said. ‘Then there are the holiday kids [who’ve fallen off] bikes or skateboards.’
In one recent case, a teenage girl presented with extensive sunburn that had initially been treated in the pharmacy. Several days later, she returned with worsening symptoms.
‘She came back about 5 days later and it looked like she’d picked up a bacterial infection from broken skin.’
At that point, Ms Davies referred the patient to a doctor, recognising that pharmacy management was no longer sufficient. ‘It had just gone too far for anything that we could do for her.’
Marine-related skin reactions are another frequent presentation, particularly sea lice, which can ‘get caught in between the swimmers and their skin’.
Management usually involves antihistamines, topical corticosteroids and practical advice to reduce symptoms.
‘You tell them to keep the area cool,’ Ms Davies said. ‘Anything that makes them hotter will make it worse.’
In most cases, these conditions can be managed entirely in-store, allowing patients to avoid medical appointments during short stays.
‘But there's a lot of regular customers and we still have all the Webster-paks among other things to manage,’ she said.
Rebecca Davies[/caption]
‘You get people that aren’t used to the sun that come in with sunburn,’ Ms Davies said.
Children feature prominently, particularly those visiting from interstate or overseas – presenting with significant sunburn, dehydration or injuries sustained during outdoor play.
‘The kids that come from places that aren’t used to the beaches come in with the sunburn,’ she said. ‘Then there are the holiday kids [who’ve fallen off] bikes or skateboards.’
In one recent case, a teenage girl presented with extensive sunburn that had initially been treated in the pharmacy. Several days later, she returned with worsening symptoms.
‘She came back about 5 days later and it looked like she’d picked up a bacterial infection from broken skin.’
At that point, Ms Davies referred the patient to a doctor, recognising that pharmacy management was no longer sufficient. ‘It had just gone too far for anything that we could do for her.’
Marine-related skin reactions are another frequent presentation, particularly sea lice, which can ‘get caught in between the swimmers and their skin’.
Management usually involves antihistamines, topical corticosteroids and practical advice to reduce symptoms.
‘You tell them to keep the area cool,’ Ms Davies said. ‘Anything that makes them hotter will make it worse.’
In most cases, these conditions can be managed entirely in-store, allowing patients to avoid medical appointments during short stays.
‘But there's a lot of regular customers and we still have all the Webster-paks among other things to manage,’ she said.
Managing forgotten medicines
Beyond acute injuries and skin conditions, medicine continuity for holidaymakers is one of the most complex challenges Ms Davies faces.
Tourists frequently arrive without sufficient medicine supply, having forgotten it at home or miscalculating how long they would be away.
‘it’s quite satisfying to help someone who is on their holidays by keeping it running smoothly and taking the stress out of it.'
rebecca davies
‘If the customer has a regular pharmacy at home, we can contact that pharmacy,’ she said. ‘They can fax scripts and post the originals.’
Electronic prescriptions have made this process significantly easier.
‘With eScripts, it’s really easy to sign them up to the Active Script List and have access to all their eScripts online,’ Ms Davies said.
However, not all situations are quickly resolved.
‘I had one customer the other day who’d left her medicine at home and didn’t have a script,’ she said.
The medicine was venlafaxine, which should not be stopped abruptly.
In this particular situation, the best course of action was for the patient to arrange an urgent medical consultation with their regular GP, or via an online telehealth provider if necessary.
‘I encourage people to stay with their regular doctor. But there are times when those services are very useful.’
Managing medicines for visiting patients often requires Ms Davies to look beyond her own dispensary.
‘If we don’t have the medication and it’s for someone passing through, ordering it in isn’t always a possibility, because the person might move on before it comes in,’ she said.
‘So we’ll ring the other pharmacies around to see if they’ve got it and direct the patient there. It’s just about trying to source the medication for the patient before they move on.’
Expanded scope makes a difference on holiday
Expanded scope of practice services have proven particularly valuable in a tourist-heavy setting, especially pharmacist-led treatment for uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs).
‘Patients with symptoms of a UTI who have come here for the weekend can come into the pharmacy quite distressed,’ Ms Davies said. ‘The symptoms of the infection really disrupt how they get through the day and they’re not familiar with the area or the doctors.’
Being able to assess and treat eligible patients in the pharmacy can significantly reduce discomfort and disruption.
‘It definitely puts them at ease when we go through that, that list of when we can and can't supply,’ Ms Davies said. ‘We can say, “Yes, we can help you”.’
For visitors, the impact is immediate.
‘They’re not wasting 24 to 48 hours trying to figure out where to go,’ she said. ‘It makes a big difference to their holiday.’
According to Ms Davies, community awareness of pharmacist UTI services has increased, with many patients now presenting specifically requesting assessment rather than symptom-only treatments.
‘More people come in already knowing that the service exists rather than asking for Ural,’ she said.
Staffing for constant demand
Maintaining service quality during sustained busy periods requires careful staff management.
‘Sometimes the owner puts more staff on over the holiday period. Because obviously there’s going to be an influx of tourists, there’s a couple of extra staff we can call on,’ Ms Davies said.
‘The business also supports private clinics, so we have access to extra staff we can call on during the day if things start to back up.’
The pharmacy relies on a mix of permanent staff, casual pharmacists, students and graduates to manage peaks. Having experienced casual staff who can be called in at short notice is particularly valuable.
‘We’re lucky to have someone we can call on who used to be a permanent employee and now works casually,’ she said.
Despite the intensity, Ms Davies finds the work highly rewarding.
‘It definitely tests your knowledge on how to navigate certain situations,’ she said. ‘And it’s quite satisfying to help someone who is on their holidays by keeping it running smoothly and taking the stress out of it.’
For pharmacists considering a move to a coastal area, Rebecca sees beachside practice as challenging but professionally enriching.
‘It offers lots of different scenarios for helping patients compared to your regular customer coming in with the same things from month to month,’ she said. ‘And there’s lots of opportunities for problem-solving.’
Help patients avoid serious sunburn by completing the AP CPD: Sun safety, don’t feel the burn.
Image licensed under Creative Commons.
[post_title] => Practising pharmacy where others vacation
[post_excerpt] => Holiday crowds bring unique clinical challenges for beachside pharmacy practice, from sun exposure injuries to urgent medicine gaps.
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => practising-pharmacy-where-others-vacation
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-21 15:53:15
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-21 04:53:15
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31206
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => Practising pharmacy where others vacation
[title] => Practising pharmacy where others vacation
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/practising-pharmacy-where-others-vacation/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31209
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31190
[post_author] => 3410
[post_date] => 2026-01-19 11:11:00
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-19 00:11:00
[post_content] => A recent systematic review published in the BMJ has reignited debate about what happens when patients stop taking glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) and related GLP-1–based incretin therapies.
The analysis found that weight often returns quickly once treatment is discontinued – in some cases faster than with other weight-loss interventions.
And it’s not just weight that rebounds. Cardiometabolic risk markers, including blood pressure, blood glucose and blood lipids, were also found to revert towards pre-treatment levels.
As prescribing of these medicines continues to rise, the findings raise a broader question: should patients be starting these medicines in the first place?
AP spoke with experts to unpack the evidence.
Weight regain predictable, but not the real problem
Professor Clare Collins, Professor of Nutrition and Dietetics at the University of Newcastle, said the pattern of rapid weight regain following cessation was entirely unsurprising.
‘This is exactly what you would expect,’ she said.
[caption id="attachment_31196" align="aligncenter" width="400"] Professor Clare Collins[/caption]
For Prof Collins, the findings reinforce a core principle of chronic disease management: when an effective treatment is withdrawn, the condition it was controlling usually returns.
‘If someone stops taking antihypertensives, what happens? Their blood pressure goes back up,’ she said.
Professor Clare Collins[/caption]
For Prof Collins, the findings reinforce a core principle of chronic disease management: when an effective treatment is withdrawn, the condition it was controlling usually returns.
‘If someone stops taking antihypertensives, what happens? Their blood pressure goes back up,’ she said.
‘While predictable, the deterioration back to baseline is why we need to be thinking much more carefully about what is needed for long-term maintenance.'
Prof clare collins
While weight regain attracts headlines, Prof Collins said the more clinically concerning signal is the deterioration in metabolic markers once treatment ceases.
‘While predictable, the deterioration back to baseline is why we need to be thinking much more carefully about what is needed for long-term maintenance.’
Not a sign of treatment failure
Associate Professor Trevor Steward, Director of the Melbourne School of Psychological Sciences’ Brain and Mental Health Hub, agrees that the rebound effect reflects how GLP-1 RA medicines work, rather than a failure of the drugs or patient behaviour.
Instead of creating permanent physiological change, GLP-1 RAs amplify hormonal signals that already exist in the body – particularly those involved in appetite regulation, digestion and satiety. The benefits seen during treatment depend on sustained exposure to these hormones.
[caption id="attachment_31197" align="aligncenter" width="400"] Associate Professor Trevor Steward[/caption]
‘That's why we see this rapid rebound effect of people experiencing weight gain when they stop using them, because there’s no longer increased circulating levels of hormones impacting their different body systems,’ A/Prof Steward said.
However, the mechanisms behind the accelerated regain are not yet fully understood.
‘Some indications are that while these newer medications help people lose weight faster, they may cause a stronger slingshot effect,’ he said.
Prof Collins points to emerging evidence suggesting incretin therapies cross the blood–brain barrier, influencing reward pathways linked to appetite and environmental cues to eat.
‘For example, if you go to the supermarket for a loaf of bread and come back with donuts too – that’s what’s referred to as “food noise”,’ she said. ‘Some people say this [noise] really goes down when using these therapies.’
When treatment is withdrawn, the surrounding food environment can quickly reassert itself. This is where tapering, behavioural support and nutrition strategies become critical.
‘It may be that people are more receptive to maintenance support programs as they’re tapering or finding out what their maintenance medication dose is,’ she said. ‘If they’re aware of that point, they’ll recognise when the food noise starts again.’
Associate Professor Trevor Steward[/caption]
‘That's why we see this rapid rebound effect of people experiencing weight gain when they stop using them, because there’s no longer increased circulating levels of hormones impacting their different body systems,’ A/Prof Steward said.
However, the mechanisms behind the accelerated regain are not yet fully understood.
‘Some indications are that while these newer medications help people lose weight faster, they may cause a stronger slingshot effect,’ he said.
Prof Collins points to emerging evidence suggesting incretin therapies cross the blood–brain barrier, influencing reward pathways linked to appetite and environmental cues to eat.
‘For example, if you go to the supermarket for a loaf of bread and come back with donuts too – that’s what’s referred to as “food noise”,’ she said. ‘Some people say this [noise] really goes down when using these therapies.’
When treatment is withdrawn, the surrounding food environment can quickly reassert itself. This is where tapering, behavioural support and nutrition strategies become critical.
‘It may be that people are more receptive to maintenance support programs as they’re tapering or finding out what their maintenance medication dose is,’ she said. ‘If they’re aware of that point, they’ll recognise when the food noise starts again.’
Nutrition: the missing variable
Prof Collins recently led a systematic review which highlighted that changes in dietary intake and nutrition remain largely invisible in incretin trials.
‘Of all the phase three trials, only two actually measured and reported what people ate,’ she said.
Most trials provided standardised advice but did not collect data on dietary intake, leaving clinicians to infer how appetite suppression, nausea and early satiety shaped eating patterns over time.
‘They mostly worked with people to identify dietary changes that would remove about 2,000 kilojoules a day – enough to trigger weight loss,’ she said.
But reduced intake doesn’t automatically equate to improved diet quality or nutrient adequacy, with micronutrient deficiencies and loss of lean mass emerging if nutrition isn’t actively monitored.
With frequent patient contact, Prof Collins believes pharmacists are uniquely placed to identify emerging problems, intervene early and support appropriate referral to dietitians for medical nutrition therapy.
‘[And] if pharmacy staff are trained, they can say, “Hang on a minute, you need to talk to the pharmacist”.’
The University of Newcastle also has a suite of resources pharmacists could direct patients to, including a healthy eating quiz and obesity management podcast, available here.
When visible deterioration or rapid weight loss appears, referral becomes essential. ‘Once you think, “this person is fading before our eyes”, that’s when you alert the GP and refer to a dietitian,’ Prof Collins said.
Supporting persistence with therapy also plays a role in outcomes.
‘The main benefit isn’t weight – it’s metabolic health,’ she said. ‘Helping people manage [adverse] effects supports continuation.’
As weight loss occurs, pharmacists should also be alert to the need to review other medicines.
‘If someone is dropping weight rapidly, blood sugars and blood pressure can fall,’ she said. ‘There are also rare but potentially severe complications – pancreatitis, gallstones, bowel obstruction and non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy,’ she said. ‘Staying well hydrated is critical – urine should look straw-coloured.’
Playing the long game
A/Prof Steward said there’s now sufficient evidence to normalise weight regain after cessation. And given the established risks associated with long-term obesity, he suggests continued therapy may represent a lower-risk option for some patients.
‘As we know, having a very high BMI for a long period of time confers its own levels of risks in terms of cardiovascular disease and other issues,’ he said. ‘So [many clinicians] think it's worth staying on these [medicines] long term as opposed to the potential risk of weight [regain].’
For people with repeated cycles of weight loss and regain, A/Prof Steward said GLP-1 RAs are increasingly being understood as potentially lifelong treatments – similar to medicines used for other chronic conditions.
‘Clinicians want clearer evidence around tapering and maintenance – and right now, they’re operating in the dark.'
A/prof trevor steward
‘I recently had a conversation with someone who has lost over 50 kilograms three times in her life,’ he said. ‘After a sustained period of lifestyle change, the weight still comes back. She would rather stay on these medicines for life than put her body through that cycle again.’
As use expands, A/Prof Steward emphasised the importance of clarifying intent and expectations before treatment begins.
‘It's really important to have that conversation with a pharmacist or GP about whether they want to make that commitment to potentially taking these long term,’ he said.
This also creates space to explore motivations for initiating therapy.
‘A lot of people are taking these medications for non-health related reasons, e.g. if they have a wedding coming up,’ A/Prof Steward said.
‘So it's really worth emphasising that these medications are serious drugs that impact the entire body, and it's not something that should be frivolously taken for the purpose of losing a few kg in a month – only to just have them come back.’
While Prof Collins doesn’t think the BMJ findings should deter prescribing, she said cost must be contextualised early – particularly as maintenance strategies continue to evolve. This may include lower costs associated with food and other medicines.
‘If you're improving your weight-related health, how much would medical visits have cost if your health hadn’t improved?’ she said. ‘These medications are a long-term cost, like a car or a mobile phone. We also don't yet know whether, for some people, they may be able to have periods where they don't take it and then reinitiate at lower doses again.’
With potential PBS listings and new formulations on the horizon, A/Prof Steward said clinical messaging will need to evolve alongside the evidence.
‘Over half a million Australians are now taking these medicines,’ he said. ‘Clinicians want clearer evidence around tapering and maintenance – and right now, they’re operating in the dark.’
For more information, read the AP CPD article Weight loss management.
[post_title] => Are GLP-1 RAs becoming lifelong medicines?
[post_excerpt] => A recent systematic review has reignited debate about what happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 RAs and related incretin therapies.
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => are-glp-1-ras-becoming-lifelong-medicines
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-19 15:35:39
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-19 04:35:39
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31190
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => Are GLP-1 RAs becoming lifelong medicines?
[title] => Are GLP-1 RAs becoming lifelong medicines?
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/are-glp-1-ras-becoming-lifelong-medicines/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31192
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31238
[post_author] => 6804
[post_date] => 2026-01-28 14:00:38
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-28 03:00:38
[post_content] => Australia's Minister for Health has announced a National Medicines Record. What is it, and what will it achieve?
Medicine safety has long depended on pharmacists making critical decisions with incomplete information. As prescribing becomes increasingly fragmented across face-to-face care, telehealth and digital platforms, those gaps are widening – with serious consequences for patients.
Reforms announced by Minister for Health and Ageing Mark Butler this morning aim to address this issue, eventually leading to a National Medicines Record.
The announcement follows advocacy by Alison Collins after the death of her daughter Erin, who died in 2024 after being prescribed medicines through multiple digital health platforms without a complete view of her medical history.
Erin’s story
Erin was 24 years old and had been taking multiple medicines for her mental health. She had been hospitalised multiple times for problems stemming from medicine misuse and was placed on daily staged supply pickup of her medicines.
The hospital care teams were so concerned they placed multiple warning messages in her My Health Record. However, these warnings were not accessed by telehealth services or local pharmacies prior to her fatal overdose.
Erin’s case highlighted systemic vulnerabilities that pharmacists have warned about for years, particularly as digital prescribing expands faster than the safeguards designed to support safe, coordinated care.
The first step
Initially, the reforms would require all medicines information from online prescribers to be uploaded to My Health Record For pharmacists, this will make a fuller picture of all the medicines a patient has been prescribed more visible. This is critical given the increasing number of prescribers an individual may have with the rise of telehealth and condition-specific providers.
Under the proposed changes, medicines prescribed and dispensed through online platforms – including the clinical context for prescribing – would be made available through My Health Record. This is intended to help reduce the risk of medicine errors, adverse drug reactions and inappropriate use by ensuring healthcare professionals have access to more complete and timely information.
The path to a National Medicines Record
The reforms also commit the Government to designing and developing a National Medicines Record using existing digital health infrastructure, including electronic prescribing, the Active Script List and My Health Record.
While details are still emerging, the proposal has the potential to address a core challenge for pharmacists: how to identify and resolve medicines-related risks without a reliable, up-to-date picture of a patient’s full medicines history.
Welcoming the announcement, PSA National President Professor Mark Naunton MPS noted it aligns with the profession's long standing advocacy.
'Pharmacists have consistently sought better-connected digital health systems to improve patient safety with medicines. It’s something PSA has been advocating for over many years, including through our flagship medicine safety report series,” Prof. Naunton said.
'Access to a more complete and reliable medicines record has the potential to significantly improve patient safety and strengthen clinical decision-making.'
'The announcement is fully aligned with PSA’s ongoing advocacy to improve medicines safety systems and ensure pharmacists are supported as medicines experts across all settings of care,' he continued.
'PSA will engage in the consultation for these proposals and continue to work with the Government to support system improvements that make medicine use in Australia safer.'
A consultation period is now underway to guide the inclusion of medicines information from all online prescribers by default, with the first phase expected to be completed by December 2026. The Government has also flagged ongoing enhancements to the 1800MEDICARE app to support medicines management.
[post_title] => What a National Medicines Record might mean for patient safety and pharmacy practice
[post_excerpt] => Australia's Minister for Health has announced a National Medicines Record. What is it, and what will it achieve?
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => towards-a-national-medicines-record
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-30 16:02:41
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-30 05:02:41
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31238
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => What a National Medicines Record might mean for patient safety and pharmacy practice
[title] => What a National Medicines Record might mean for patient safety and pharmacy practice
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/towards-a-national-medicines-record/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31240
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31221
[post_author] => 3410
[post_date] => 2026-01-27 10:42:14
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-26 23:42:14
[post_content] => Community pharmacist Deborah Williams reflects on 7 years working at the Chemist Warehouse Australian Open pop-up pharmacy, sharing what makes event-based practice unique, the presentations she sees most often, and why adaptability is essential outside the traditional pharmacy setting.
How is running a pop-up pharmacy at the Australian Open different from your day-to-day practice?
The pop-up pharmacy at the Australian Open (AO) differs from practising in a community pharmacy such as Eltham, primarily because of the tools and therapeutic options available.
At the AO, we don’t have access to Schedule 4 medicines, and there are even additional restrictions imposed on over-the-counter medicines by the tournament. Certain Pharmacist Only products we would routinely recommend in a community setting aren’t permitted, particularly medicines that may cause drowsiness or could be perceived as performance-enhancing. This significantly changes how symptom management is approached.
The patient demographic is also very different. We see a large number of international visitors and cruise passengers who may only be in Australia briefly and often present with immediate, short-term needs – for example, sleep disruption, pain, minor illness, dehydration or general discomfort after long travel. There are frequent situations where a medicine that would be clinically appropriate in a normal pharmacy setting simply isn’t an option at the AO, so you have to think laterally and focus on non-sedating, non-restricted alternatives and practical advice. The pop-up pharmacy also operates with a deliberately limited range selection, so you rely far more on clinical judgement, counselling and problem-solving than product depth.
Despite these constraints, the service has been extremely well received. In earlier years, many people were genuinely surprised that a pharmacy service was available at all, and the level of appreciation was very high. Over time, as the service has become established, patrons have come to actively expect that level of healthcare support onsite – which speaks to how valuable it has proven to be.
Ultimately, while the setting is very different, the core role remains the same: providing accessible, safe short-term healthcare support. At the AO, that simply requires a more adaptive and creative approach within tighter boundaries.
Why did you first put your hand up for this roster 7 years ago?
Largely because tennis is a big part of our family life. My two daughters are avid tennis players, and I’ve spent a lot of time travelling with them to tournaments – both around Australia and internationally. So the opportunity to be involved in the AO and to experience tennis from a different perspective was very appealing.
At the time, the chance to be part of a pop-up pharmacy within a major sporting event felt unique. Working in an environment where the energy is high and where people are genuinely excited to be there was a strong motivator. It also offered the opportunity to step outside the traditional four walls of community pharmacy and apply my skills in a different, fast-paced setting.
[caption id="attachment_31227" align="aligncenter" width="600"] Deborah Williams at the Chemist Warehouse Australian Open pop-up pharmacy[/caption]
I’ve previously worked as a pharmacist at other large-scale events, including the Grand Prix and the Colour Run, and I’ve always enjoyed that style of practice. You see different patient groups and presentations, and there’s a strong focus on immediate, practical healthcare support. Combining that type of work with a sport that’s already such a big part of my life made the AO an easy decision.
Deborah Williams at the Chemist Warehouse Australian Open pop-up pharmacy[/caption]
I’ve previously worked as a pharmacist at other large-scale events, including the Grand Prix and the Colour Run, and I’ve always enjoyed that style of practice. You see different patient groups and presentations, and there’s a strong focus on immediate, practical healthcare support. Combining that type of work with a sport that’s already such a big part of my life made the AO an easy decision.
What are the most common presentations you deal with?
They vary from year to year, often reflecting broader environmental and public health factors.
In early years, respiratory presentations were prominent, with high demand for salbutamol due to smoke exposure following severe bushfires. During the COVID-19 pandemic, testing-related requests and symptomatic presentations dominated, with many people seeking advice for fever, cough, fatigue and isolation management. Across all years, heat-related conditions are consistently common. We see significant sunburn, dehydration, headaches and heat exhaustion – with many patrons initially attributing symptoms solely to sun exposure. Being able to distinguish between sunburn, heat exhaustion and early heat stroke is a critical part of the role.
Other frequent presentations include viral infections, gastrointestinal upset, reflux and heartburn related to food and alcohol consumption – as well as general pain and discomfort from long days on site.
Overall, the role involves managing acute, short-term presentations in a high-heat, high-activity environment, where timely assessment, clear advice and appropriate escalation are essential.
What has been your best experience working at the AO?
The cumulative nature of the role over many years. Being invited back repeatedly reflects the value of having pharmacists in a high-profile, high-pressure environment.
But one particularly rewarding aspect has been the behind-the-scenes clinical role. While players rarely attend the pharmacy, their support staff and assistants frequently seek advice on their behalf. That often involves real-time discussions, sometimes over the phone, where clinical judgement, clarity and discretion are critical. The trust placed in pharmacists in those moments is significant.
Knowing that the advice provided may contribute, even in a small way, to a player’s comfort, recovery or ability to perform is professionally satisfying. It reinforces the role of pharmacists as accessible healthcare professionals who can deliver practical, timely support in environments where precision matters.
What are the most popular products with tennis fans?
Those that address the practical realities of spending long hours outdoors and walking significant distances, often in warm conditions.
Blister management products are consistently in high demand, particularly protective dressings and treatments for foot friction. Sun exposure also drives strong demand for post-sunburn and skin-soothing treatments, as well as products to manage heat-related discomfort.
Gastrointestinal support is another common category, with antacid and reflux treatments frequently requested, often related to food choices, heat and prolonged time on site.
Hydration support products are also very popular, particularly oral rehydration formulations for patrons experiencing fatigue, headaches or dehydration. Simple analgesics for pain and headache management are frequently requested as well.
‘Knowing that the advice provided may contribute, even in a small way, to a player’s comfort, recovery or ability to perform is professionally satisfying.'
deborah williams
And convenient nutritional snacks, particularly protein bars, are consistently popular, reflecting the need for quick, portable options that support energy levels throughout the day. Personal care essentials such as deodorant are also commonly requested, given the length and physical nature of the event.
Who is your favourite tennis player?
For many years my favourite player was Rafael Nadal. Beyond his extraordinary achievements on court, what stood out most was his character. He has a genuine never-say-die attitude, combined with humility and respect for everyone around him. Behind the scenes he was approachable, carried his own bags, acknowledged volunteers and staff, and treated people with quiet respect – which left a lasting impression.
More recently, I’ve really enjoyed watching Alex de Minaur. His speed, work rate and relentless court coverage are exceptional – and he brings an intensity and competitiveness that’s exciting to watch. He represents a very grounded, hardworking style of tennis that resonates strongly with Australian fans.
Do you have any tips for pharmacists working at the AO this summer?
Embrace the environment and enjoy the opportunity to practise pharmacy in a different setting. The atmosphere is energetic and positive, and people genuinely want your advice, making the role both enjoyable and rewarding.
From a professional perspective, be prepared to think beyond products. With a diverse, transient population, many interactions involve problem-solving rather than dispensing. That may mean offering practical health advice, directing people to appropriate medical services, or helping them navigate local healthcare options.
It’s also important to remember that you are representing both your profession and the event itself, so clear communication, professionalism and sound judgement matter. Finally, take the time to experience the event. Use breaks to watch some tennis or explore the precinct. Being part of the Australian Open is a unique opportunity, and enjoying the atmosphere helps you bring energy and perspective back into your role.
[post_title] => Pharmacy on centre court
[post_excerpt] => Limited medicines options and time-critical presentations push pharmacists at the Australian Open to practise at the top of their skills.
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => pharmacy-on-centre-court
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-27 15:01:46
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-27 04:01:46
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31221
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => Pharmacy on centre court
[title] => Pharmacy on centre court
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/pharmacy-on-centre-court/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31226
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31216
[post_author] => 9164
[post_date] => 2026-01-27 09:50:51
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-26 22:50:51
[post_content] => The PSA congratulates Emeritus Professor Colin Burton Chapman and Dipak Sanghvi of Victoria on being appointed a Member of the Order of Australia (AM) as part of the 2026 Australia Day Honours.
Emeritus Prof Colin Chapman has been recognised with the AM for significant service to pharmacy and pharmaceutical science research, education and practice.
Mr Sanghvi was recognised with the AM for significant service to community health through governance and board roles.
The PSA also extended its congratulations to Rhys Hollington London, Bruce Vincent Townsend, and Maurice Alan Renshaw on being awarded the Medal of the Order of Australia (OAM).
Mr Hollington London has been recognised with the OAM for service to the community of Wynyard, Tasmania.
Mr Townsend was recognised with the OAM for service to the community of Raymond Terrace, NSW.
Mr Renshaw, also from NSW, was recognised with the OAM for service to the pharmaceutical industry.
The PSA National President Professor Mark Naunton MPS acknowledged the high honour of this recognition and thanked the recipients for their previous and ongoing contributions to the pharmacy profession.
‘It is evident that pharmacists play a vital role in their communities and the healthcare system. To have multiple pharmacists recognised on the prestigious Australia Day Honours List is a phenomenal outcome,’ Prof Naunton said.
‘On behalf of PSA and the pharmacy profession, I would like to extend my congratulations to Emeritus Prof Chapman, Mr Sanghvi, Mr Hollington London, Mr Vincent and Mr Renshaw on their well-deserved recognition.’
[post_title] => National recognition for pharmacists on Australia Day
[post_excerpt] => The PSA congratulates the pharmacists who were recognised as part on this year's Australia Day Honours List.
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => national-recognition-for-pharmacists-on-australia-day
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-27 15:02:15
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-27 04:02:15
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31216
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => National recognition for pharmacists on Australia Day
[title] => National recognition for pharmacists on Australia Day
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/national-recognition-for-pharmacists-on-australia-day/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31220
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31206
[post_author] => 3410
[post_date] => 2026-01-21 10:52:56
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-20 23:52:56
[post_content] => Holiday crowds bring unique clinical challenges, testing pharmacists’ problem-solving skills from sun exposure injuries to urgent medicine gaps.
In many metropolitan areas, January is a lull period for pharmacists – as city dwellers head out of town to beat the heat and reset for the year ahead. But not so in many regional beachside areas, with pharmacies experiencing a steady uptick in visiting clientele, as Rebecca Davies, who works as a community pharmacist in Cotton Tree on Queensland's Sunshine Coast, would attest.
‘Where I'm working at the moment is right on the beach, so it's literally busy all the time,’ said Ms Davies, who was formerly based in Mona Vale on Sydney’s Northern Beaches. ‘I wouldn't say there's ever a quiet time, as in the winter, we still get people coming up from the southern states for holidays.’
With a caravan park stationed down the road, nearby units that are typically rented out during peak holiday periods and warm weather year-round, it’s a matter of balancing the holiday trade that’s passing through with regular customers.
A clinical mix by the sea
Alongside routine dispensing and chronic disease management for locals, managing beach-related enquiries and conditions is a part of everyday practice.
Over-the-counter demand increases during holiday periods, with visitors seeking sunscreens, beach equipment and first-aid items, with many presentations requiring pharmacist oversight.
[caption id="attachment_31212" align="aligncenter" width="441"] Rebecca Davies[/caption]
‘You get people that aren’t used to the sun that come in with sunburn,’ Ms Davies said.
Children feature prominently, particularly those visiting from interstate or overseas – presenting with significant sunburn, dehydration or injuries sustained during outdoor play.
‘The kids that come from places that aren’t used to the beaches come in with the sunburn,’ she said. ‘Then there are the holiday kids [who’ve fallen off] bikes or skateboards.’
In one recent case, a teenage girl presented with extensive sunburn that had initially been treated in the pharmacy. Several days later, she returned with worsening symptoms.
‘She came back about 5 days later and it looked like she’d picked up a bacterial infection from broken skin.’
At that point, Ms Davies referred the patient to a doctor, recognising that pharmacy management was no longer sufficient. ‘It had just gone too far for anything that we could do for her.’
Marine-related skin reactions are another frequent presentation, particularly sea lice, which can ‘get caught in between the swimmers and their skin’.
Management usually involves antihistamines, topical corticosteroids and practical advice to reduce symptoms.
‘You tell them to keep the area cool,’ Ms Davies said. ‘Anything that makes them hotter will make it worse.’
In most cases, these conditions can be managed entirely in-store, allowing patients to avoid medical appointments during short stays.
‘But there's a lot of regular customers and we still have all the Webster-paks among other things to manage,’ she said.
Rebecca Davies[/caption]
‘You get people that aren’t used to the sun that come in with sunburn,’ Ms Davies said.
Children feature prominently, particularly those visiting from interstate or overseas – presenting with significant sunburn, dehydration or injuries sustained during outdoor play.
‘The kids that come from places that aren’t used to the beaches come in with the sunburn,’ she said. ‘Then there are the holiday kids [who’ve fallen off] bikes or skateboards.’
In one recent case, a teenage girl presented with extensive sunburn that had initially been treated in the pharmacy. Several days later, she returned with worsening symptoms.
‘She came back about 5 days later and it looked like she’d picked up a bacterial infection from broken skin.’
At that point, Ms Davies referred the patient to a doctor, recognising that pharmacy management was no longer sufficient. ‘It had just gone too far for anything that we could do for her.’
Marine-related skin reactions are another frequent presentation, particularly sea lice, which can ‘get caught in between the swimmers and their skin’.
Management usually involves antihistamines, topical corticosteroids and practical advice to reduce symptoms.
‘You tell them to keep the area cool,’ Ms Davies said. ‘Anything that makes them hotter will make it worse.’
In most cases, these conditions can be managed entirely in-store, allowing patients to avoid medical appointments during short stays.
‘But there's a lot of regular customers and we still have all the Webster-paks among other things to manage,’ she said.
Managing forgotten medicines
Beyond acute injuries and skin conditions, medicine continuity for holidaymakers is one of the most complex challenges Ms Davies faces.
Tourists frequently arrive without sufficient medicine supply, having forgotten it at home or miscalculating how long they would be away.
‘it’s quite satisfying to help someone who is on their holidays by keeping it running smoothly and taking the stress out of it.'
rebecca davies
‘If the customer has a regular pharmacy at home, we can contact that pharmacy,’ she said. ‘They can fax scripts and post the originals.’
Electronic prescriptions have made this process significantly easier.
‘With eScripts, it’s really easy to sign them up to the Active Script List and have access to all their eScripts online,’ Ms Davies said.
However, not all situations are quickly resolved.
‘I had one customer the other day who’d left her medicine at home and didn’t have a script,’ she said.
The medicine was venlafaxine, which should not be stopped abruptly.
In this particular situation, the best course of action was for the patient to arrange an urgent medical consultation with their regular GP, or via an online telehealth provider if necessary.
‘I encourage people to stay with their regular doctor. But there are times when those services are very useful.’
Managing medicines for visiting patients often requires Ms Davies to look beyond her own dispensary.
‘If we don’t have the medication and it’s for someone passing through, ordering it in isn’t always a possibility, because the person might move on before it comes in,’ she said.
‘So we’ll ring the other pharmacies around to see if they’ve got it and direct the patient there. It’s just about trying to source the medication for the patient before they move on.’
Expanded scope makes a difference on holiday
Expanded scope of practice services have proven particularly valuable in a tourist-heavy setting, especially pharmacist-led treatment for uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs).
‘Patients with symptoms of a UTI who have come here for the weekend can come into the pharmacy quite distressed,’ Ms Davies said. ‘The symptoms of the infection really disrupt how they get through the day and they’re not familiar with the area or the doctors.’
Being able to assess and treat eligible patients in the pharmacy can significantly reduce discomfort and disruption.
‘It definitely puts them at ease when we go through that, that list of when we can and can't supply,’ Ms Davies said. ‘We can say, “Yes, we can help you”.’
For visitors, the impact is immediate.
‘They’re not wasting 24 to 48 hours trying to figure out where to go,’ she said. ‘It makes a big difference to their holiday.’
According to Ms Davies, community awareness of pharmacist UTI services has increased, with many patients now presenting specifically requesting assessment rather than symptom-only treatments.
‘More people come in already knowing that the service exists rather than asking for Ural,’ she said.
Staffing for constant demand
Maintaining service quality during sustained busy periods requires careful staff management.
‘Sometimes the owner puts more staff on over the holiday period. Because obviously there’s going to be an influx of tourists, there’s a couple of extra staff we can call on,’ Ms Davies said.
‘The business also supports private clinics, so we have access to extra staff we can call on during the day if things start to back up.’
The pharmacy relies on a mix of permanent staff, casual pharmacists, students and graduates to manage peaks. Having experienced casual staff who can be called in at short notice is particularly valuable.
‘We’re lucky to have someone we can call on who used to be a permanent employee and now works casually,’ she said.
Despite the intensity, Ms Davies finds the work highly rewarding.
‘It definitely tests your knowledge on how to navigate certain situations,’ she said. ‘And it’s quite satisfying to help someone who is on their holidays by keeping it running smoothly and taking the stress out of it.’
For pharmacists considering a move to a coastal area, Rebecca sees beachside practice as challenging but professionally enriching.
‘It offers lots of different scenarios for helping patients compared to your regular customer coming in with the same things from month to month,’ she said. ‘And there’s lots of opportunities for problem-solving.’
Help patients avoid serious sunburn by completing the AP CPD: Sun safety, don’t feel the burn.
Image licensed under Creative Commons.
[post_title] => Practising pharmacy where others vacation
[post_excerpt] => Holiday crowds bring unique clinical challenges for beachside pharmacy practice, from sun exposure injuries to urgent medicine gaps.
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => practising-pharmacy-where-others-vacation
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-21 15:53:15
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-21 04:53:15
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31206
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => Practising pharmacy where others vacation
[title] => Practising pharmacy where others vacation
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/practising-pharmacy-where-others-vacation/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31209
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31190
[post_author] => 3410
[post_date] => 2026-01-19 11:11:00
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-19 00:11:00
[post_content] => A recent systematic review published in the BMJ has reignited debate about what happens when patients stop taking glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) and related GLP-1–based incretin therapies.
The analysis found that weight often returns quickly once treatment is discontinued – in some cases faster than with other weight-loss interventions.
And it’s not just weight that rebounds. Cardiometabolic risk markers, including blood pressure, blood glucose and blood lipids, were also found to revert towards pre-treatment levels.
As prescribing of these medicines continues to rise, the findings raise a broader question: should patients be starting these medicines in the first place?
AP spoke with experts to unpack the evidence.
Weight regain predictable, but not the real problem
Professor Clare Collins, Professor of Nutrition and Dietetics at the University of Newcastle, said the pattern of rapid weight regain following cessation was entirely unsurprising.
‘This is exactly what you would expect,’ she said.
[caption id="attachment_31196" align="aligncenter" width="400"] Professor Clare Collins[/caption]
For Prof Collins, the findings reinforce a core principle of chronic disease management: when an effective treatment is withdrawn, the condition it was controlling usually returns.
‘If someone stops taking antihypertensives, what happens? Their blood pressure goes back up,’ she said.
Professor Clare Collins[/caption]
For Prof Collins, the findings reinforce a core principle of chronic disease management: when an effective treatment is withdrawn, the condition it was controlling usually returns.
‘If someone stops taking antihypertensives, what happens? Their blood pressure goes back up,’ she said.
‘While predictable, the deterioration back to baseline is why we need to be thinking much more carefully about what is needed for long-term maintenance.'
Prof clare collins
While weight regain attracts headlines, Prof Collins said the more clinically concerning signal is the deterioration in metabolic markers once treatment ceases.
‘While predictable, the deterioration back to baseline is why we need to be thinking much more carefully about what is needed for long-term maintenance.’
Not a sign of treatment failure
Associate Professor Trevor Steward, Director of the Melbourne School of Psychological Sciences’ Brain and Mental Health Hub, agrees that the rebound effect reflects how GLP-1 RA medicines work, rather than a failure of the drugs or patient behaviour.
Instead of creating permanent physiological change, GLP-1 RAs amplify hormonal signals that already exist in the body – particularly those involved in appetite regulation, digestion and satiety. The benefits seen during treatment depend on sustained exposure to these hormones.
[caption id="attachment_31197" align="aligncenter" width="400"] Associate Professor Trevor Steward[/caption]
‘That's why we see this rapid rebound effect of people experiencing weight gain when they stop using them, because there’s no longer increased circulating levels of hormones impacting their different body systems,’ A/Prof Steward said.
However, the mechanisms behind the accelerated regain are not yet fully understood.
‘Some indications are that while these newer medications help people lose weight faster, they may cause a stronger slingshot effect,’ he said.
Prof Collins points to emerging evidence suggesting incretin therapies cross the blood–brain barrier, influencing reward pathways linked to appetite and environmental cues to eat.
‘For example, if you go to the supermarket for a loaf of bread and come back with donuts too – that’s what’s referred to as “food noise”,’ she said. ‘Some people say this [noise] really goes down when using these therapies.’
When treatment is withdrawn, the surrounding food environment can quickly reassert itself. This is where tapering, behavioural support and nutrition strategies become critical.
‘It may be that people are more receptive to maintenance support programs as they’re tapering or finding out what their maintenance medication dose is,’ she said. ‘If they’re aware of that point, they’ll recognise when the food noise starts again.’
Associate Professor Trevor Steward[/caption]
‘That's why we see this rapid rebound effect of people experiencing weight gain when they stop using them, because there’s no longer increased circulating levels of hormones impacting their different body systems,’ A/Prof Steward said.
However, the mechanisms behind the accelerated regain are not yet fully understood.
‘Some indications are that while these newer medications help people lose weight faster, they may cause a stronger slingshot effect,’ he said.
Prof Collins points to emerging evidence suggesting incretin therapies cross the blood–brain barrier, influencing reward pathways linked to appetite and environmental cues to eat.
‘For example, if you go to the supermarket for a loaf of bread and come back with donuts too – that’s what’s referred to as “food noise”,’ she said. ‘Some people say this [noise] really goes down when using these therapies.’
When treatment is withdrawn, the surrounding food environment can quickly reassert itself. This is where tapering, behavioural support and nutrition strategies become critical.
‘It may be that people are more receptive to maintenance support programs as they’re tapering or finding out what their maintenance medication dose is,’ she said. ‘If they’re aware of that point, they’ll recognise when the food noise starts again.’
Nutrition: the missing variable
Prof Collins recently led a systematic review which highlighted that changes in dietary intake and nutrition remain largely invisible in incretin trials.
‘Of all the phase three trials, only two actually measured and reported what people ate,’ she said.
Most trials provided standardised advice but did not collect data on dietary intake, leaving clinicians to infer how appetite suppression, nausea and early satiety shaped eating patterns over time.
‘They mostly worked with people to identify dietary changes that would remove about 2,000 kilojoules a day – enough to trigger weight loss,’ she said.
But reduced intake doesn’t automatically equate to improved diet quality or nutrient adequacy, with micronutrient deficiencies and loss of lean mass emerging if nutrition isn’t actively monitored.
With frequent patient contact, Prof Collins believes pharmacists are uniquely placed to identify emerging problems, intervene early and support appropriate referral to dietitians for medical nutrition therapy.
‘[And] if pharmacy staff are trained, they can say, “Hang on a minute, you need to talk to the pharmacist”.’
The University of Newcastle also has a suite of resources pharmacists could direct patients to, including a healthy eating quiz and obesity management podcast, available here.
When visible deterioration or rapid weight loss appears, referral becomes essential. ‘Once you think, “this person is fading before our eyes”, that’s when you alert the GP and refer to a dietitian,’ Prof Collins said.
Supporting persistence with therapy also plays a role in outcomes.
‘The main benefit isn’t weight – it’s metabolic health,’ she said. ‘Helping people manage [adverse] effects supports continuation.’
As weight loss occurs, pharmacists should also be alert to the need to review other medicines.
‘If someone is dropping weight rapidly, blood sugars and blood pressure can fall,’ she said. ‘There are also rare but potentially severe complications – pancreatitis, gallstones, bowel obstruction and non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy,’ she said. ‘Staying well hydrated is critical – urine should look straw-coloured.’
Playing the long game
A/Prof Steward said there’s now sufficient evidence to normalise weight regain after cessation. And given the established risks associated with long-term obesity, he suggests continued therapy may represent a lower-risk option for some patients.
‘As we know, having a very high BMI for a long period of time confers its own levels of risks in terms of cardiovascular disease and other issues,’ he said. ‘So [many clinicians] think it's worth staying on these [medicines] long term as opposed to the potential risk of weight [regain].’
For people with repeated cycles of weight loss and regain, A/Prof Steward said GLP-1 RAs are increasingly being understood as potentially lifelong treatments – similar to medicines used for other chronic conditions.
‘Clinicians want clearer evidence around tapering and maintenance – and right now, they’re operating in the dark.'
A/prof trevor steward
‘I recently had a conversation with someone who has lost over 50 kilograms three times in her life,’ he said. ‘After a sustained period of lifestyle change, the weight still comes back. She would rather stay on these medicines for life than put her body through that cycle again.’
As use expands, A/Prof Steward emphasised the importance of clarifying intent and expectations before treatment begins.
‘It's really important to have that conversation with a pharmacist or GP about whether they want to make that commitment to potentially taking these long term,’ he said.
This also creates space to explore motivations for initiating therapy.
‘A lot of people are taking these medications for non-health related reasons, e.g. if they have a wedding coming up,’ A/Prof Steward said.
‘So it's really worth emphasising that these medications are serious drugs that impact the entire body, and it's not something that should be frivolously taken for the purpose of losing a few kg in a month – only to just have them come back.’
While Prof Collins doesn’t think the BMJ findings should deter prescribing, she said cost must be contextualised early – particularly as maintenance strategies continue to evolve. This may include lower costs associated with food and other medicines.
‘If you're improving your weight-related health, how much would medical visits have cost if your health hadn’t improved?’ she said. ‘These medications are a long-term cost, like a car or a mobile phone. We also don't yet know whether, for some people, they may be able to have periods where they don't take it and then reinitiate at lower doses again.’
With potential PBS listings and new formulations on the horizon, A/Prof Steward said clinical messaging will need to evolve alongside the evidence.
‘Over half a million Australians are now taking these medicines,’ he said. ‘Clinicians want clearer evidence around tapering and maintenance – and right now, they’re operating in the dark.’
For more information, read the AP CPD article Weight loss management.
[post_title] => Are GLP-1 RAs becoming lifelong medicines?
[post_excerpt] => A recent systematic review has reignited debate about what happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 RAs and related incretin therapies.
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => are-glp-1-ras-becoming-lifelong-medicines
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-19 15:35:39
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-19 04:35:39
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31190
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => Are GLP-1 RAs becoming lifelong medicines?
[title] => Are GLP-1 RAs becoming lifelong medicines?
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/are-glp-1-ras-becoming-lifelong-medicines/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31192
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31238
[post_author] => 6804
[post_date] => 2026-01-28 14:00:38
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-28 03:00:38
[post_content] => Australia's Minister for Health has announced a National Medicines Record. What is it, and what will it achieve?
Medicine safety has long depended on pharmacists making critical decisions with incomplete information. As prescribing becomes increasingly fragmented across face-to-face care, telehealth and digital platforms, those gaps are widening – with serious consequences for patients.
Reforms announced by Minister for Health and Ageing Mark Butler this morning aim to address this issue, eventually leading to a National Medicines Record.
The announcement follows advocacy by Alison Collins after the death of her daughter Erin, who died in 2024 after being prescribed medicines through multiple digital health platforms without a complete view of her medical history.
Erin’s story
Erin was 24 years old and had been taking multiple medicines for her mental health. She had been hospitalised multiple times for problems stemming from medicine misuse and was placed on daily staged supply pickup of her medicines.
The hospital care teams were so concerned they placed multiple warning messages in her My Health Record. However, these warnings were not accessed by telehealth services or local pharmacies prior to her fatal overdose.
Erin’s case highlighted systemic vulnerabilities that pharmacists have warned about for years, particularly as digital prescribing expands faster than the safeguards designed to support safe, coordinated care.
The first step
Initially, the reforms would require all medicines information from online prescribers to be uploaded to My Health Record For pharmacists, this will make a fuller picture of all the medicines a patient has been prescribed more visible. This is critical given the increasing number of prescribers an individual may have with the rise of telehealth and condition-specific providers.
Under the proposed changes, medicines prescribed and dispensed through online platforms – including the clinical context for prescribing – would be made available through My Health Record. This is intended to help reduce the risk of medicine errors, adverse drug reactions and inappropriate use by ensuring healthcare professionals have access to more complete and timely information.
The path to a National Medicines Record
The reforms also commit the Government to designing and developing a National Medicines Record using existing digital health infrastructure, including electronic prescribing, the Active Script List and My Health Record.
While details are still emerging, the proposal has the potential to address a core challenge for pharmacists: how to identify and resolve medicines-related risks without a reliable, up-to-date picture of a patient’s full medicines history.
Welcoming the announcement, PSA National President Professor Mark Naunton MPS noted it aligns with the profession's long standing advocacy.
'Pharmacists have consistently sought better-connected digital health systems to improve patient safety with medicines. It’s something PSA has been advocating for over many years, including through our flagship medicine safety report series,” Prof. Naunton said.
'Access to a more complete and reliable medicines record has the potential to significantly improve patient safety and strengthen clinical decision-making.'
'The announcement is fully aligned with PSA’s ongoing advocacy to improve medicines safety systems and ensure pharmacists are supported as medicines experts across all settings of care,' he continued.
'PSA will engage in the consultation for these proposals and continue to work with the Government to support system improvements that make medicine use in Australia safer.'
A consultation period is now underway to guide the inclusion of medicines information from all online prescribers by default, with the first phase expected to be completed by December 2026. The Government has also flagged ongoing enhancements to the 1800MEDICARE app to support medicines management.
[post_title] => What a National Medicines Record might mean for patient safety and pharmacy practice
[post_excerpt] => Australia's Minister for Health has announced a National Medicines Record. What is it, and what will it achieve?
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => towards-a-national-medicines-record
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-30 16:02:41
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-30 05:02:41
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31238
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => What a National Medicines Record might mean for patient safety and pharmacy practice
[title] => What a National Medicines Record might mean for patient safety and pharmacy practice
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/towards-a-national-medicines-record/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31240
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31221
[post_author] => 3410
[post_date] => 2026-01-27 10:42:14
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-26 23:42:14
[post_content] => Community pharmacist Deborah Williams reflects on 7 years working at the Chemist Warehouse Australian Open pop-up pharmacy, sharing what makes event-based practice unique, the presentations she sees most often, and why adaptability is essential outside the traditional pharmacy setting.
How is running a pop-up pharmacy at the Australian Open different from your day-to-day practice?
The pop-up pharmacy at the Australian Open (AO) differs from practising in a community pharmacy such as Eltham, primarily because of the tools and therapeutic options available.
At the AO, we don’t have access to Schedule 4 medicines, and there are even additional restrictions imposed on over-the-counter medicines by the tournament. Certain Pharmacist Only products we would routinely recommend in a community setting aren’t permitted, particularly medicines that may cause drowsiness or could be perceived as performance-enhancing. This significantly changes how symptom management is approached.
The patient demographic is also very different. We see a large number of international visitors and cruise passengers who may only be in Australia briefly and often present with immediate, short-term needs – for example, sleep disruption, pain, minor illness, dehydration or general discomfort after long travel. There are frequent situations where a medicine that would be clinically appropriate in a normal pharmacy setting simply isn’t an option at the AO, so you have to think laterally and focus on non-sedating, non-restricted alternatives and practical advice. The pop-up pharmacy also operates with a deliberately limited range selection, so you rely far more on clinical judgement, counselling and problem-solving than product depth.
Despite these constraints, the service has been extremely well received. In earlier years, many people were genuinely surprised that a pharmacy service was available at all, and the level of appreciation was very high. Over time, as the service has become established, patrons have come to actively expect that level of healthcare support onsite – which speaks to how valuable it has proven to be.
Ultimately, while the setting is very different, the core role remains the same: providing accessible, safe short-term healthcare support. At the AO, that simply requires a more adaptive and creative approach within tighter boundaries.
Why did you first put your hand up for this roster 7 years ago?
Largely because tennis is a big part of our family life. My two daughters are avid tennis players, and I’ve spent a lot of time travelling with them to tournaments – both around Australia and internationally. So the opportunity to be involved in the AO and to experience tennis from a different perspective was very appealing.
At the time, the chance to be part of a pop-up pharmacy within a major sporting event felt unique. Working in an environment where the energy is high and where people are genuinely excited to be there was a strong motivator. It also offered the opportunity to step outside the traditional four walls of community pharmacy and apply my skills in a different, fast-paced setting.
[caption id="attachment_31227" align="aligncenter" width="600"] Deborah Williams at the Chemist Warehouse Australian Open pop-up pharmacy[/caption]
I’ve previously worked as a pharmacist at other large-scale events, including the Grand Prix and the Colour Run, and I’ve always enjoyed that style of practice. You see different patient groups and presentations, and there’s a strong focus on immediate, practical healthcare support. Combining that type of work with a sport that’s already such a big part of my life made the AO an easy decision.
Deborah Williams at the Chemist Warehouse Australian Open pop-up pharmacy[/caption]
I’ve previously worked as a pharmacist at other large-scale events, including the Grand Prix and the Colour Run, and I’ve always enjoyed that style of practice. You see different patient groups and presentations, and there’s a strong focus on immediate, practical healthcare support. Combining that type of work with a sport that’s already such a big part of my life made the AO an easy decision.
What are the most common presentations you deal with?
They vary from year to year, often reflecting broader environmental and public health factors.
In early years, respiratory presentations were prominent, with high demand for salbutamol due to smoke exposure following severe bushfires. During the COVID-19 pandemic, testing-related requests and symptomatic presentations dominated, with many people seeking advice for fever, cough, fatigue and isolation management. Across all years, heat-related conditions are consistently common. We see significant sunburn, dehydration, headaches and heat exhaustion – with many patrons initially attributing symptoms solely to sun exposure. Being able to distinguish between sunburn, heat exhaustion and early heat stroke is a critical part of the role.
Other frequent presentations include viral infections, gastrointestinal upset, reflux and heartburn related to food and alcohol consumption – as well as general pain and discomfort from long days on site.
Overall, the role involves managing acute, short-term presentations in a high-heat, high-activity environment, where timely assessment, clear advice and appropriate escalation are essential.
What has been your best experience working at the AO?
The cumulative nature of the role over many years. Being invited back repeatedly reflects the value of having pharmacists in a high-profile, high-pressure environment.
But one particularly rewarding aspect has been the behind-the-scenes clinical role. While players rarely attend the pharmacy, their support staff and assistants frequently seek advice on their behalf. That often involves real-time discussions, sometimes over the phone, where clinical judgement, clarity and discretion are critical. The trust placed in pharmacists in those moments is significant.
Knowing that the advice provided may contribute, even in a small way, to a player’s comfort, recovery or ability to perform is professionally satisfying. It reinforces the role of pharmacists as accessible healthcare professionals who can deliver practical, timely support in environments where precision matters.
What are the most popular products with tennis fans?
Those that address the practical realities of spending long hours outdoors and walking significant distances, often in warm conditions.
Blister management products are consistently in high demand, particularly protective dressings and treatments for foot friction. Sun exposure also drives strong demand for post-sunburn and skin-soothing treatments, as well as products to manage heat-related discomfort.
Gastrointestinal support is another common category, with antacid and reflux treatments frequently requested, often related to food choices, heat and prolonged time on site.
Hydration support products are also very popular, particularly oral rehydration formulations for patrons experiencing fatigue, headaches or dehydration. Simple analgesics for pain and headache management are frequently requested as well.
‘Knowing that the advice provided may contribute, even in a small way, to a player’s comfort, recovery or ability to perform is professionally satisfying.'
deborah williams
And convenient nutritional snacks, particularly protein bars, are consistently popular, reflecting the need for quick, portable options that support energy levels throughout the day. Personal care essentials such as deodorant are also commonly requested, given the length and physical nature of the event.
Who is your favourite tennis player?
For many years my favourite player was Rafael Nadal. Beyond his extraordinary achievements on court, what stood out most was his character. He has a genuine never-say-die attitude, combined with humility and respect for everyone around him. Behind the scenes he was approachable, carried his own bags, acknowledged volunteers and staff, and treated people with quiet respect – which left a lasting impression.
More recently, I’ve really enjoyed watching Alex de Minaur. His speed, work rate and relentless court coverage are exceptional – and he brings an intensity and competitiveness that’s exciting to watch. He represents a very grounded, hardworking style of tennis that resonates strongly with Australian fans.
Do you have any tips for pharmacists working at the AO this summer?
Embrace the environment and enjoy the opportunity to practise pharmacy in a different setting. The atmosphere is energetic and positive, and people genuinely want your advice, making the role both enjoyable and rewarding.
From a professional perspective, be prepared to think beyond products. With a diverse, transient population, many interactions involve problem-solving rather than dispensing. That may mean offering practical health advice, directing people to appropriate medical services, or helping them navigate local healthcare options.
It’s also important to remember that you are representing both your profession and the event itself, so clear communication, professionalism and sound judgement matter. Finally, take the time to experience the event. Use breaks to watch some tennis or explore the precinct. Being part of the Australian Open is a unique opportunity, and enjoying the atmosphere helps you bring energy and perspective back into your role.
[post_title] => Pharmacy on centre court
[post_excerpt] => Limited medicines options and time-critical presentations push pharmacists at the Australian Open to practise at the top of their skills.
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => pharmacy-on-centre-court
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-27 15:01:46
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-27 04:01:46
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31221
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => Pharmacy on centre court
[title] => Pharmacy on centre court
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/pharmacy-on-centre-court/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31226
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31216
[post_author] => 9164
[post_date] => 2026-01-27 09:50:51
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-26 22:50:51
[post_content] => The PSA congratulates Emeritus Professor Colin Burton Chapman and Dipak Sanghvi of Victoria on being appointed a Member of the Order of Australia (AM) as part of the 2026 Australia Day Honours.
Emeritus Prof Colin Chapman has been recognised with the AM for significant service to pharmacy and pharmaceutical science research, education and practice.
Mr Sanghvi was recognised with the AM for significant service to community health through governance and board roles.
The PSA also extended its congratulations to Rhys Hollington London, Bruce Vincent Townsend, and Maurice Alan Renshaw on being awarded the Medal of the Order of Australia (OAM).
Mr Hollington London has been recognised with the OAM for service to the community of Wynyard, Tasmania.
Mr Townsend was recognised with the OAM for service to the community of Raymond Terrace, NSW.
Mr Renshaw, also from NSW, was recognised with the OAM for service to the pharmaceutical industry.
The PSA National President Professor Mark Naunton MPS acknowledged the high honour of this recognition and thanked the recipients for their previous and ongoing contributions to the pharmacy profession.
‘It is evident that pharmacists play a vital role in their communities and the healthcare system. To have multiple pharmacists recognised on the prestigious Australia Day Honours List is a phenomenal outcome,’ Prof Naunton said.
‘On behalf of PSA and the pharmacy profession, I would like to extend my congratulations to Emeritus Prof Chapman, Mr Sanghvi, Mr Hollington London, Mr Vincent and Mr Renshaw on their well-deserved recognition.’
[post_title] => National recognition for pharmacists on Australia Day
[post_excerpt] => The PSA congratulates the pharmacists who were recognised as part on this year's Australia Day Honours List.
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => national-recognition-for-pharmacists-on-australia-day
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-27 15:02:15
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-27 04:02:15
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31216
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => National recognition for pharmacists on Australia Day
[title] => National recognition for pharmacists on Australia Day
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/national-recognition-for-pharmacists-on-australia-day/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31220
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31206
[post_author] => 3410
[post_date] => 2026-01-21 10:52:56
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-20 23:52:56
[post_content] => Holiday crowds bring unique clinical challenges, testing pharmacists’ problem-solving skills from sun exposure injuries to urgent medicine gaps.
In many metropolitan areas, January is a lull period for pharmacists – as city dwellers head out of town to beat the heat and reset for the year ahead. But not so in many regional beachside areas, with pharmacies experiencing a steady uptick in visiting clientele, as Rebecca Davies, who works as a community pharmacist in Cotton Tree on Queensland's Sunshine Coast, would attest.
‘Where I'm working at the moment is right on the beach, so it's literally busy all the time,’ said Ms Davies, who was formerly based in Mona Vale on Sydney’s Northern Beaches. ‘I wouldn't say there's ever a quiet time, as in the winter, we still get people coming up from the southern states for holidays.’
With a caravan park stationed down the road, nearby units that are typically rented out during peak holiday periods and warm weather year-round, it’s a matter of balancing the holiday trade that’s passing through with regular customers.
A clinical mix by the sea
Alongside routine dispensing and chronic disease management for locals, managing beach-related enquiries and conditions is a part of everyday practice.
Over-the-counter demand increases during holiday periods, with visitors seeking sunscreens, beach equipment and first-aid items, with many presentations requiring pharmacist oversight.
[caption id="attachment_31212" align="aligncenter" width="441"] Rebecca Davies[/caption]
‘You get people that aren’t used to the sun that come in with sunburn,’ Ms Davies said.
Children feature prominently, particularly those visiting from interstate or overseas – presenting with significant sunburn, dehydration or injuries sustained during outdoor play.
‘The kids that come from places that aren’t used to the beaches come in with the sunburn,’ she said. ‘Then there are the holiday kids [who’ve fallen off] bikes or skateboards.’
In one recent case, a teenage girl presented with extensive sunburn that had initially been treated in the pharmacy. Several days later, she returned with worsening symptoms.
‘She came back about 5 days later and it looked like she’d picked up a bacterial infection from broken skin.’
At that point, Ms Davies referred the patient to a doctor, recognising that pharmacy management was no longer sufficient. ‘It had just gone too far for anything that we could do for her.’
Marine-related skin reactions are another frequent presentation, particularly sea lice, which can ‘get caught in between the swimmers and their skin’.
Management usually involves antihistamines, topical corticosteroids and practical advice to reduce symptoms.
‘You tell them to keep the area cool,’ Ms Davies said. ‘Anything that makes them hotter will make it worse.’
In most cases, these conditions can be managed entirely in-store, allowing patients to avoid medical appointments during short stays.
‘But there's a lot of regular customers and we still have all the Webster-paks among other things to manage,’ she said.
Rebecca Davies[/caption]
‘You get people that aren’t used to the sun that come in with sunburn,’ Ms Davies said.
Children feature prominently, particularly those visiting from interstate or overseas – presenting with significant sunburn, dehydration or injuries sustained during outdoor play.
‘The kids that come from places that aren’t used to the beaches come in with the sunburn,’ she said. ‘Then there are the holiday kids [who’ve fallen off] bikes or skateboards.’
In one recent case, a teenage girl presented with extensive sunburn that had initially been treated in the pharmacy. Several days later, she returned with worsening symptoms.
‘She came back about 5 days later and it looked like she’d picked up a bacterial infection from broken skin.’
At that point, Ms Davies referred the patient to a doctor, recognising that pharmacy management was no longer sufficient. ‘It had just gone too far for anything that we could do for her.’
Marine-related skin reactions are another frequent presentation, particularly sea lice, which can ‘get caught in between the swimmers and their skin’.
Management usually involves antihistamines, topical corticosteroids and practical advice to reduce symptoms.
‘You tell them to keep the area cool,’ Ms Davies said. ‘Anything that makes them hotter will make it worse.’
In most cases, these conditions can be managed entirely in-store, allowing patients to avoid medical appointments during short stays.
‘But there's a lot of regular customers and we still have all the Webster-paks among other things to manage,’ she said.
Managing forgotten medicines
Beyond acute injuries and skin conditions, medicine continuity for holidaymakers is one of the most complex challenges Ms Davies faces.
Tourists frequently arrive without sufficient medicine supply, having forgotten it at home or miscalculating how long they would be away.
‘it’s quite satisfying to help someone who is on their holidays by keeping it running smoothly and taking the stress out of it.'
rebecca davies
‘If the customer has a regular pharmacy at home, we can contact that pharmacy,’ she said. ‘They can fax scripts and post the originals.’
Electronic prescriptions have made this process significantly easier.
‘With eScripts, it’s really easy to sign them up to the Active Script List and have access to all their eScripts online,’ Ms Davies said.
However, not all situations are quickly resolved.
‘I had one customer the other day who’d left her medicine at home and didn’t have a script,’ she said.
The medicine was venlafaxine, which should not be stopped abruptly.
In this particular situation, the best course of action was for the patient to arrange an urgent medical consultation with their regular GP, or via an online telehealth provider if necessary.
‘I encourage people to stay with their regular doctor. But there are times when those services are very useful.’
Managing medicines for visiting patients often requires Ms Davies to look beyond her own dispensary.
‘If we don’t have the medication and it’s for someone passing through, ordering it in isn’t always a possibility, because the person might move on before it comes in,’ she said.
‘So we’ll ring the other pharmacies around to see if they’ve got it and direct the patient there. It’s just about trying to source the medication for the patient before they move on.’
Expanded scope makes a difference on holiday
Expanded scope of practice services have proven particularly valuable in a tourist-heavy setting, especially pharmacist-led treatment for uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs).
‘Patients with symptoms of a UTI who have come here for the weekend can come into the pharmacy quite distressed,’ Ms Davies said. ‘The symptoms of the infection really disrupt how they get through the day and they’re not familiar with the area or the doctors.’
Being able to assess and treat eligible patients in the pharmacy can significantly reduce discomfort and disruption.
‘It definitely puts them at ease when we go through that, that list of when we can and can't supply,’ Ms Davies said. ‘We can say, “Yes, we can help you”.’
For visitors, the impact is immediate.
‘They’re not wasting 24 to 48 hours trying to figure out where to go,’ she said. ‘It makes a big difference to their holiday.’
According to Ms Davies, community awareness of pharmacist UTI services has increased, with many patients now presenting specifically requesting assessment rather than symptom-only treatments.
‘More people come in already knowing that the service exists rather than asking for Ural,’ she said.
Staffing for constant demand
Maintaining service quality during sustained busy periods requires careful staff management.
‘Sometimes the owner puts more staff on over the holiday period. Because obviously there’s going to be an influx of tourists, there’s a couple of extra staff we can call on,’ Ms Davies said.
‘The business also supports private clinics, so we have access to extra staff we can call on during the day if things start to back up.’
The pharmacy relies on a mix of permanent staff, casual pharmacists, students and graduates to manage peaks. Having experienced casual staff who can be called in at short notice is particularly valuable.
‘We’re lucky to have someone we can call on who used to be a permanent employee and now works casually,’ she said.
Despite the intensity, Ms Davies finds the work highly rewarding.
‘It definitely tests your knowledge on how to navigate certain situations,’ she said. ‘And it’s quite satisfying to help someone who is on their holidays by keeping it running smoothly and taking the stress out of it.’
For pharmacists considering a move to a coastal area, Rebecca sees beachside practice as challenging but professionally enriching.
‘It offers lots of different scenarios for helping patients compared to your regular customer coming in with the same things from month to month,’ she said. ‘And there’s lots of opportunities for problem-solving.’
Help patients avoid serious sunburn by completing the AP CPD: Sun safety, don’t feel the burn.
Image licensed under Creative Commons.
[post_title] => Practising pharmacy where others vacation
[post_excerpt] => Holiday crowds bring unique clinical challenges for beachside pharmacy practice, from sun exposure injuries to urgent medicine gaps.
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => practising-pharmacy-where-others-vacation
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-21 15:53:15
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-21 04:53:15
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31206
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => Practising pharmacy where others vacation
[title] => Practising pharmacy where others vacation
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/practising-pharmacy-where-others-vacation/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31209
[authorType] =>
)
td_module_mega_menu Object
(
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 31190
[post_author] => 3410
[post_date] => 2026-01-19 11:11:00
[post_date_gmt] => 2026-01-19 00:11:00
[post_content] => A recent systematic review published in the BMJ has reignited debate about what happens when patients stop taking glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) and related GLP-1–based incretin therapies.
The analysis found that weight often returns quickly once treatment is discontinued – in some cases faster than with other weight-loss interventions.
And it’s not just weight that rebounds. Cardiometabolic risk markers, including blood pressure, blood glucose and blood lipids, were also found to revert towards pre-treatment levels.
As prescribing of these medicines continues to rise, the findings raise a broader question: should patients be starting these medicines in the first place?
AP spoke with experts to unpack the evidence.
Weight regain predictable, but not the real problem
Professor Clare Collins, Professor of Nutrition and Dietetics at the University of Newcastle, said the pattern of rapid weight regain following cessation was entirely unsurprising.
‘This is exactly what you would expect,’ she said.
[caption id="attachment_31196" align="aligncenter" width="400"] Professor Clare Collins[/caption]
For Prof Collins, the findings reinforce a core principle of chronic disease management: when an effective treatment is withdrawn, the condition it was controlling usually returns.
‘If someone stops taking antihypertensives, what happens? Their blood pressure goes back up,’ she said.
Professor Clare Collins[/caption]
For Prof Collins, the findings reinforce a core principle of chronic disease management: when an effective treatment is withdrawn, the condition it was controlling usually returns.
‘If someone stops taking antihypertensives, what happens? Their blood pressure goes back up,’ she said.
‘While predictable, the deterioration back to baseline is why we need to be thinking much more carefully about what is needed for long-term maintenance.'
Prof clare collins
While weight regain attracts headlines, Prof Collins said the more clinically concerning signal is the deterioration in metabolic markers once treatment ceases.
‘While predictable, the deterioration back to baseline is why we need to be thinking much more carefully about what is needed for long-term maintenance.’
Not a sign of treatment failure
Associate Professor Trevor Steward, Director of the Melbourne School of Psychological Sciences’ Brain and Mental Health Hub, agrees that the rebound effect reflects how GLP-1 RA medicines work, rather than a failure of the drugs or patient behaviour.
Instead of creating permanent physiological change, GLP-1 RAs amplify hormonal signals that already exist in the body – particularly those involved in appetite regulation, digestion and satiety. The benefits seen during treatment depend on sustained exposure to these hormones.
[caption id="attachment_31197" align="aligncenter" width="400"] Associate Professor Trevor Steward[/caption]
‘That's why we see this rapid rebound effect of people experiencing weight gain when they stop using them, because there’s no longer increased circulating levels of hormones impacting their different body systems,’ A/Prof Steward said.
However, the mechanisms behind the accelerated regain are not yet fully understood.
‘Some indications are that while these newer medications help people lose weight faster, they may cause a stronger slingshot effect,’ he said.
Prof Collins points to emerging evidence suggesting incretin therapies cross the blood–brain barrier, influencing reward pathways linked to appetite and environmental cues to eat.
‘For example, if you go to the supermarket for a loaf of bread and come back with donuts too – that’s what’s referred to as “food noise”,’ she said. ‘Some people say this [noise] really goes down when using these therapies.’
When treatment is withdrawn, the surrounding food environment can quickly reassert itself. This is where tapering, behavioural support and nutrition strategies become critical.
‘It may be that people are more receptive to maintenance support programs as they’re tapering or finding out what their maintenance medication dose is,’ she said. ‘If they’re aware of that point, they’ll recognise when the food noise starts again.’
Associate Professor Trevor Steward[/caption]
‘That's why we see this rapid rebound effect of people experiencing weight gain when they stop using them, because there’s no longer increased circulating levels of hormones impacting their different body systems,’ A/Prof Steward said.
However, the mechanisms behind the accelerated regain are not yet fully understood.
‘Some indications are that while these newer medications help people lose weight faster, they may cause a stronger slingshot effect,’ he said.
Prof Collins points to emerging evidence suggesting incretin therapies cross the blood–brain barrier, influencing reward pathways linked to appetite and environmental cues to eat.
‘For example, if you go to the supermarket for a loaf of bread and come back with donuts too – that’s what’s referred to as “food noise”,’ she said. ‘Some people say this [noise] really goes down when using these therapies.’
When treatment is withdrawn, the surrounding food environment can quickly reassert itself. This is where tapering, behavioural support and nutrition strategies become critical.
‘It may be that people are more receptive to maintenance support programs as they’re tapering or finding out what their maintenance medication dose is,’ she said. ‘If they’re aware of that point, they’ll recognise when the food noise starts again.’
Nutrition: the missing variable
Prof Collins recently led a systematic review which highlighted that changes in dietary intake and nutrition remain largely invisible in incretin trials.
‘Of all the phase three trials, only two actually measured and reported what people ate,’ she said.
Most trials provided standardised advice but did not collect data on dietary intake, leaving clinicians to infer how appetite suppression, nausea and early satiety shaped eating patterns over time.
‘They mostly worked with people to identify dietary changes that would remove about 2,000 kilojoules a day – enough to trigger weight loss,’ she said.
But reduced intake doesn’t automatically equate to improved diet quality or nutrient adequacy, with micronutrient deficiencies and loss of lean mass emerging if nutrition isn’t actively monitored.
With frequent patient contact, Prof Collins believes pharmacists are uniquely placed to identify emerging problems, intervene early and support appropriate referral to dietitians for medical nutrition therapy.
‘[And] if pharmacy staff are trained, they can say, “Hang on a minute, you need to talk to the pharmacist”.’
The University of Newcastle also has a suite of resources pharmacists could direct patients to, including a healthy eating quiz and obesity management podcast, available here.
When visible deterioration or rapid weight loss appears, referral becomes essential. ‘Once you think, “this person is fading before our eyes”, that’s when you alert the GP and refer to a dietitian,’ Prof Collins said.
Supporting persistence with therapy also plays a role in outcomes.
‘The main benefit isn’t weight – it’s metabolic health,’ she said. ‘Helping people manage [adverse] effects supports continuation.’
As weight loss occurs, pharmacists should also be alert to the need to review other medicines.
‘If someone is dropping weight rapidly, blood sugars and blood pressure can fall,’ she said. ‘There are also rare but potentially severe complications – pancreatitis, gallstones, bowel obstruction and non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy,’ she said. ‘Staying well hydrated is critical – urine should look straw-coloured.’
Playing the long game
A/Prof Steward said there’s now sufficient evidence to normalise weight regain after cessation. And given the established risks associated with long-term obesity, he suggests continued therapy may represent a lower-risk option for some patients.
‘As we know, having a very high BMI for a long period of time confers its own levels of risks in terms of cardiovascular disease and other issues,’ he said. ‘So [many clinicians] think it's worth staying on these [medicines] long term as opposed to the potential risk of weight [regain].’
For people with repeated cycles of weight loss and regain, A/Prof Steward said GLP-1 RAs are increasingly being understood as potentially lifelong treatments – similar to medicines used for other chronic conditions.
‘Clinicians want clearer evidence around tapering and maintenance – and right now, they’re operating in the dark.'
A/prof trevor steward
‘I recently had a conversation with someone who has lost over 50 kilograms three times in her life,’ he said. ‘After a sustained period of lifestyle change, the weight still comes back. She would rather stay on these medicines for life than put her body through that cycle again.’
As use expands, A/Prof Steward emphasised the importance of clarifying intent and expectations before treatment begins.
‘It's really important to have that conversation with a pharmacist or GP about whether they want to make that commitment to potentially taking these long term,’ he said.
This also creates space to explore motivations for initiating therapy.
‘A lot of people are taking these medications for non-health related reasons, e.g. if they have a wedding coming up,’ A/Prof Steward said.
‘So it's really worth emphasising that these medications are serious drugs that impact the entire body, and it's not something that should be frivolously taken for the purpose of losing a few kg in a month – only to just have them come back.’
While Prof Collins doesn’t think the BMJ findings should deter prescribing, she said cost must be contextualised early – particularly as maintenance strategies continue to evolve. This may include lower costs associated with food and other medicines.
‘If you're improving your weight-related health, how much would medical visits have cost if your health hadn’t improved?’ she said. ‘These medications are a long-term cost, like a car or a mobile phone. We also don't yet know whether, for some people, they may be able to have periods where they don't take it and then reinitiate at lower doses again.’
With potential PBS listings and new formulations on the horizon, A/Prof Steward said clinical messaging will need to evolve alongside the evidence.
‘Over half a million Australians are now taking these medicines,’ he said. ‘Clinicians want clearer evidence around tapering and maintenance – and right now, they’re operating in the dark.’
For more information, read the AP CPD article Weight loss management.
[post_title] => Are GLP-1 RAs becoming lifelong medicines?
[post_excerpt] => A recent systematic review has reignited debate about what happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 RAs and related incretin therapies.
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => open
[ping_status] => open
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => are-glp-1-ras-becoming-lifelong-medicines
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2026-01-19 15:35:39
[post_modified_gmt] => 2026-01-19 04:35:39
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/?p=31190
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[title_attribute] => Are GLP-1 RAs becoming lifelong medicines?
[title] => Are GLP-1 RAs becoming lifelong medicines?
[href] => https://www.australianpharmacist.com.au/are-glp-1-ras-becoming-lifelong-medicines/
[module_atts:td_module:private] => Array
(
)
[td_review:protected] => Array
(
)
[is_review:protected] =>
[post_thumb_id:protected] => 31192
[authorType] =>
)
Get your weekly dose of the news and research you need to help advance your practice.
Protected by Google reCAPTCHA v3.

Australian Pharmacist is the official journal for Pharmaceutical Society of Australia Ltd.