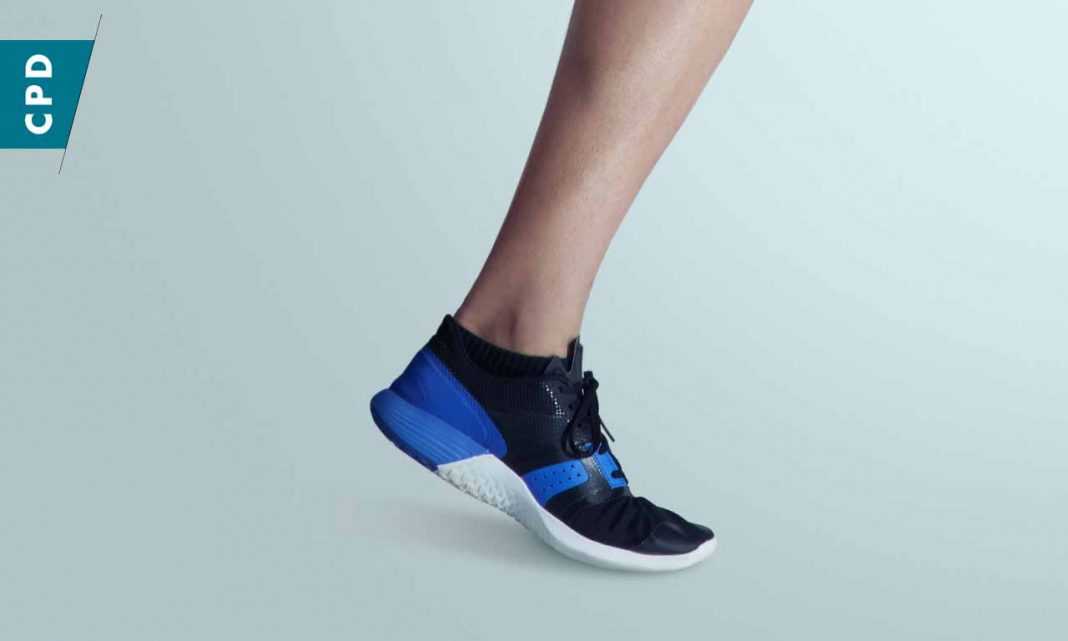
The feet and toenails are prone to a variety of infections, as they are frequently exposed to a moist environment through the regular use of footwear.
| Learning objectives
After reading this article, pharmacists should be able to:
Competencies (2016) addressed: 1.1.2, 1.1.3, 1.5.1, 1.5.2, 2.1.2, 3.1.1, 3.1.2, 3.1.3, 3.2.2, 3.2.3, 3.2.4, 3.2.5, 3.3.1, 3.3.2, 3.6.1. Competencies (2010) addressed: 1.2.1, 1.3.1, 1.3.2, 2.3.1, 2.3.2, 2.3.3, 4.2.1, 4.2.2, 4.2.3, 4.3.3, 6.1.1, 6.1.2, 6.1.3, 6.2.1, 6.2.2, 6.2.3, 6.2.4, 6.3.3, 7.1.2, 7.1.3, 7.1.4, 7.2.1, 7.2.2. |
Case scenario
Thomas (18 years old) is a budding young athlete, who comes to the pharmacy for advice regarding a rash on his feet. You discover that Thomas is currently training for several long-distance track events, and has been spending between four and five hours a day on the track, or at the gym with his coach.
Over the last few weeks, Thomas has discovered moist, red and peeling skin between his toes on both feet. In the last few days these symptoms have started to affect Thomas’ training schedule, as his toes feel irritated and itchy, and he is experiencing discomfort when wearing shoes, such as his training runners.
Want to learn more? PSA members can access the full article and assessment questions here to earn up to 1.5 Group 2 CPD credits.
Not a PSA member? Find out why more than 18,000 pharmacists choose PSA to support, advance and create opportunities for the pharmacy career and the greater pharmacy profession. Click here to join today.
The feet and toenails are prone to a variety of infections, as they are frequently exposed to a moist environment through the regular use of footwear.
| Learning objectives
After reading this article, pharmacists should be able to:
Competencies (2016) addressed: 1.1.2, 1.1.3, 1.5.1, 1.5.2, 2.1.2, 3.1.1, 3.1.2, 3.1.3, 3.2.2, 3.2.3, 3.2.4, 3.2.5, 3.3.1, 3.3.2, 3.6.1. Competencies (2010) addressed: 1.2.1, 1.3.1, 1.3.2, 2.3.1, 2.3.2, 2.3.3, 4.2.1, 4.2.2, 4.2.3, 4.3.3, 6.1.1, 6.1.2, 6.1.3, 6.2.1, 6.2.2, 6.2.3, 6.2.4, 6.3.3, 7.1.2, 7.1.3, 7.1.4, 7.2.1, 7.2.2. |
Case scenario
Thomas (18 years old) is a budding young athlete, who comes to the pharmacy for advice regarding a rash on his feet. You discover that Thomas is currently training for several long-distance track events, and has been spending between four and five hours a day on the track, or at the gym with his coach.
Over the last few weeks, Thomas has discovered moist, red and peeling skin between his toes on both feet. In the last few days these symptoms have started to affect Thomas’ training schedule, as his toes feel irritated and itchy, and he is experiencing discomfort when wearing shoes, such as his training runners.
Want to learn more? PSA members can access the full article and assessment questions here to earn up to 1.5 Group 2 CPD credits.
Not a PSA member? Find out why more than 18,000 pharmacists choose PSA to support, advance and create opportunities for the pharmacy career and the greater pharmacy profession. Click here to join today.
The feet and toenails are prone to a variety of infections, as they are frequently exposed to a moist environment through the regular use of footwear.
| Learning objectives
After reading this article, pharmacists should be able to:
Competencies (2016) addressed: 1.1.2, 1.1.3, 1.5.1, 1.5.2, 2.1.2, 3.1.1, 3.1.2, 3.1.3, 3.2.2, 3.2.3, 3.2.4, 3.2.5, 3.3.1, 3.3.2, 3.6.1. Competencies (2010) addressed: 1.2.1, 1.3.1, 1.3.2, 2.3.1, 2.3.2, 2.3.3, 4.2.1, 4.2.2, 4.2.3, 4.3.3, 6.1.1, 6.1.2, 6.1.3, 6.2.1, 6.2.2, 6.2.3, 6.2.4, 6.3.3, 7.1.2, 7.1.3, 7.1.4, 7.2.1, 7.2.2. |
Case scenario
Thomas (18 years old) is a budding young athlete, who comes to the pharmacy for advice regarding a rash on his feet. You discover that Thomas is currently training for several long-distance track events, and has been spending between four and five hours a day on the track, or at the gym with his coach.
Over the last few weeks, Thomas has discovered moist, red and peeling skin between his toes on both feet. In the last few days these symptoms have started to affect Thomas’ training schedule, as his toes feel irritated and itchy, and he is experiencing discomfort when wearing shoes, such as his training runners.
Want to learn more? PSA members can access the full article and assessment questions here to earn up to 1.5 Group 2 CPD credits.
Not a PSA member? Find out why more than 18,000 pharmacists choose PSA to support, advance and create opportunities for the pharmacy career and the greater pharmacy profession. Click here to join today.


 John Jones MPS, pharmacist immuniser and owner of My Community Pharmacy Shortland in Newcastle, NSW[/caption]
John Jones MPS, pharmacist immuniser and owner of My Community Pharmacy Shortland in Newcastle, NSW[/caption]
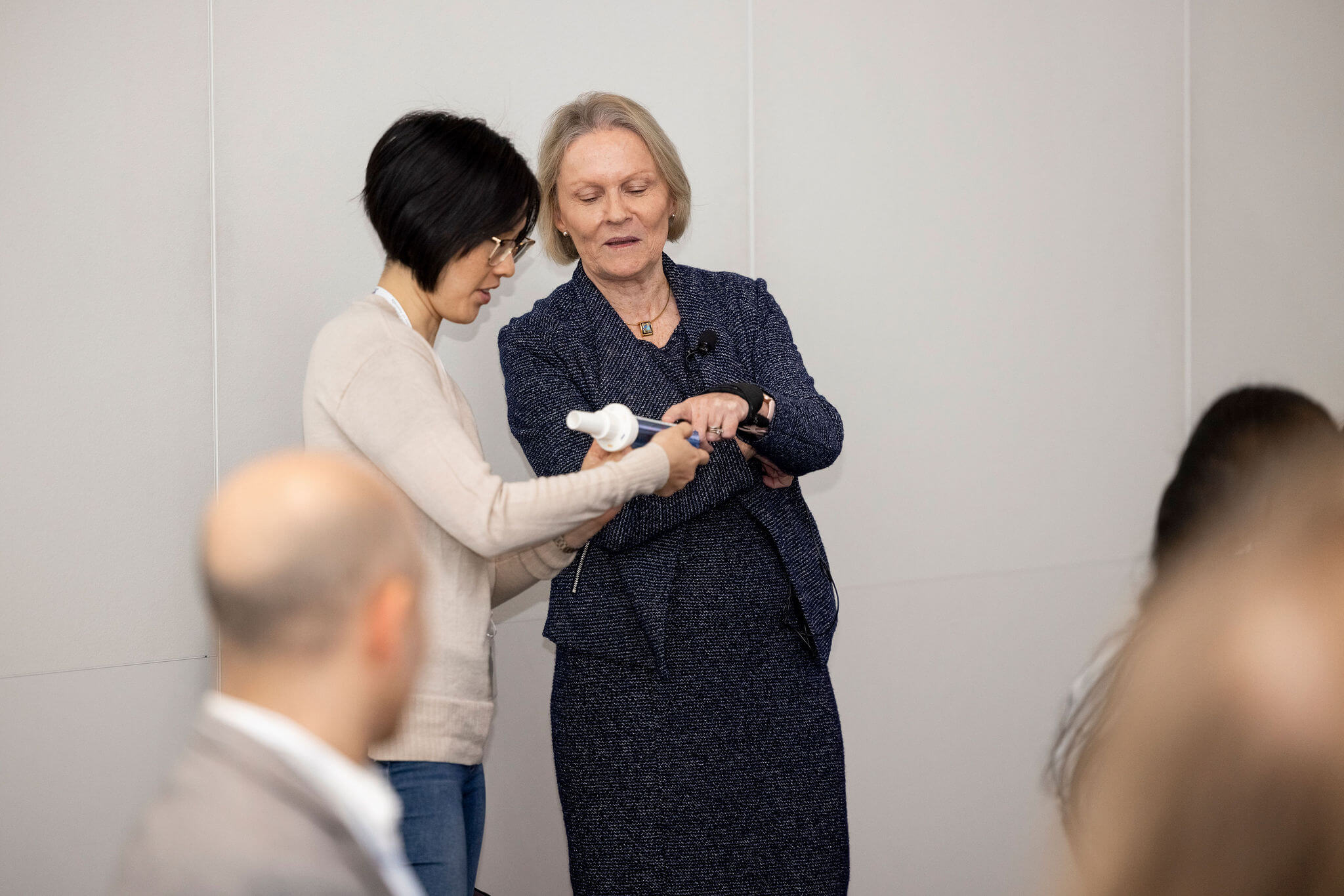

 Debbie Rigby FPS explaining how to correctly use different inhaler devices[/caption]
Debbie Rigby FPS explaining how to correctly use different inhaler devices[/caption]



 Professor Sepehr Shakib[/caption]
Professor Sepehr Shakib[/caption]

 Lee McLennan MPS[/caption]
Lee McLennan MPS[/caption]
 Dr Natalie Soulsby FPS, Adv Prac Pharm[/caption]
Dr Natalie Soulsby FPS, Adv Prac Pharm[/caption]
 Joanne Gross MPS[/caption]
Joanne Gross MPS[/caption]